- Citas Centro Médico de Caracas: Lunes, Miercoles y Viernes. Pulse el botón Agende una Cita
- Sistema de citas en linea exclusivo para Centro Medico de Caracas en San Bernardino
- Citas CMDLT: Jueves. llamar al 0212-9496243 y 9496245
- Las Emergencias son atendidas en CMDLT previa coordinacion personal al 04142708338
- Proveedor Seguros Mercantil y Sudeban

It is the birth of a baby before 37 weeks of pregnancy and occurs in 5-10% of pregnancies. The most frequent causes are spontaneous initiation of a Premature Labor, premature preterm rupture of membranes and Iatrogenic Prematurity (medical interruption of a premature pregnancy due to severe maternofetal complications in which the pregnancy can not be prolonged)
The term Premature Labor Threat implies the start of labor (birth pains) before week 37, whether or not it leads to a Preterm Birth. If this happens before week 20 we are in the presence of an Abortion. Although for many patients talking about weeks is somewhat confusing, we can not talk about months because it is imprecise when determining the causes, management and prognosis of a pregnancy complicated by this phenomenon.
Classification 2015
Prematurity: birth before week 37. Detection rate with neck less than 15 mm
- 20-27 weeks extreme prematurity 0.25%. Detection: 70%
- 28-31 weeks severe prematurity 0.25%. Detection: 45%
- 32-34 weeks moderate prematurity 0.6%. Detection: 40%
- 34-36 weeks slight prematurity 3%. Detection: 15%
- Maturity: from week 37
Subdivisions of maturity (2013):
- Early maturity 37-38.6 weeks
- Complete maturity: 39.0 to 40.6 weeks
- Late maturity: 41.0 to 41.6 weeks
- Posaturity: from week 42
Some recent publications have suggested not interrupting pregnancy before week 39 (delivery or caesarean section) due to some respiratory complications of the newborn. Later work suggests that the potential complications are similar, so the recommendation should not be so strict. In our practice, complications are so low that our interruption behavior remains the same, by week 38, and usually before the 40th. We do not use lung maturation with cesareans or deliveries before week 39 (we discuss their indication if the baby will be born before 37 weeks)
Considerations
Although every baby born before week 37 is a premature baby, the prognosis will be increasingly reserved as the Gestational Age (EG) is lower, a baby of 35 weeks has a survival of 99% but a baby of 26 weeks he has less than a 30% chance of surviving even in the best hands and in Intensive Therapy. What makes the difference? The smaller the EG of a baby, the lower its weight and the maturation of its organs, so that a very premature baby could weigh 500 to 750 grams and their organs are so poorly developed that they can not breathe on their own, digest food nor control your body temperature; These babies need to be taken to Intensive Care and be connected to artificial life systems until they grow and mature enough to be able to live by themselves, unfortunately many premature babies do not succeed and die hours, days or weeks after birth.
Prematurity is the most frequent cause of disease and mortality in newborns and the big problem that presents us to the obstetrician and his patient, is that in most of the cases we do not know who will suffer it (it has improved a little this aspect), and once it occurs, it is almost never possible to determine a cause of the problem. Despite this we know that there are many risk factors and that in some cases we can eliminate or reduce them through an adequate preventive work on the pregnant woman (Prenatal Care) and the woman who wants a future pregnancy (Preconceptional Care).
This article is an example of preventive work and aims to educate and raise concerns in pregnant women and those who are planning a pregnancy: I would be very happy if you make conscious some risks to which you could be exposed and take preventive measures in this regard, if you have doubts you could talk to your doctor in a more informed way.
The causes are very varied but those that have the most predictive value to suppose their occurrence are having had one or more Premature Births in previous pregnancies and Multiple Pregnancy. In most cases it is not possible to demonstrate a triggering cause and even treating the known causes does not guarantee that it can be avoided, but knowing what can happen and following a good prenatal control can be the difference for a premature baby.
The most important causes related to Preterm Birth are: Bacterial Infection (50% of cases), physical injury or stress causing placental damage, multiple pregnancy and environmental toxins such as environmental pollution. The common factor is an inflammatory cascade that induces labor and some fetal problems. A new drug Dextro Naloxone seems to be very efficient in inhibiting this cascade (by inhibiting the TLR4 receptor) and preventing premature birth and other fetal complications. In experimental phase in rodents, but promising.
( Chin PY et al., Sci Rep . 2016 Nov 7; 6: 36112. doi: 10.1038 / srep36112).
Maternal causes:
- Previous premature births
- Severe Maternal Disease: Hypertension, kidney disease, autoimmune diseases, Diabetes mellitus, heart disease, anemia, severe infections
- Abnormalities and / or uterine and cervical surgery, including uterine fibroids.
- Lack of Prenatal Control and preventive medical evaluation
- Extreme ages: less than 18 and over 35 years old.
- Follow-up pregnancies (less than 3 months)
- Previous abortion or threatened abortion during this pregnancy
- Severe obesity and malnutrition
- Use of cigarettes, alcohol, severe physical and / or emotional stress drugs, exhausting work
Causes of the Fetus and its Membranes:
- Multiple pregnancy
- Congenital or chromosomal abnormalities of the baby
- Premature rupture of the membranes or “water bag” (RPM)
- Amniocentesis
- Placental insufficiency
- Blood incompatibility between parents
How can I know what is happening to me?
You have less than 37 weeks and you begin to feel painful uterine contractions similar to menstrual pain, which are becoming more regular, frequent and painful. You feel belly pain with some back pain (lumbar discomfort). You can expel mucus with blood or frank loss of fluid through the vagina. You may notice a decrease in your baby’s movements.
What will my obstetrician do?
If the manifestations are clear or at least suggestive of premature labor your doctor will ask you to go immediately to the clinic, clinic or hospital and among other things you will have a Transvaginal Ultrasound to determine if the pains you have had (Uterine Contractions) have shortened and dilated your cervix (cervicometry); The vaginal touch under these conditions has been a little in disuse due to its low diagnostic sensitivity and potential complications. If the conditions so require you must be admitted to the hospital for continuous evaluation, rest and receive intravenous medication to try to stop the birth and use medicines that quickly mature your baby’s lungs in case you can not stop the delivery. Fortunately, in most cases the presence of this complication is ruled out and the mother-to-be is sent home with general indications and possibly some anti-spasmodic and relaxing medications from the uterus.
What would be the prognosis in these cases?
The prognosis depends on the fetal Gestational Age, the general maternal condition and the fetal health status. The best prognostic parameter for a baby is the highest gestational age that we can reach by stopping delivery. The most important parameters to determine the success or failure in the arrest of premature birth is the dilation of the cervix and the integrity of the membranes (Water Bag)
We know from multiple scientific studies that when the cervix has more than 3-4 cm of dilation, most of the patients stop prematurely in 48-72 hours, although it is a short time for the baby, at least it allows us to use drugs that induce maturation that improve the prognosis and the survival of the baby. When the membranes rupture before 37 weeks, the risk of infection of the baby and some problems related to circulation and fetal deformities appear. Apart from these, the rupture of the membranes is a very strong stimulus to initiate and / or maintain a premature labor. Global experience in this complex situation has shown that delivery can be stopped for 7 to 14 days.
What happens to a premature baby?
When a baby is born prematurely, its organs are not yet mature and can not survive in the extrauterine world. The first problem a premature faces is his inability to breathe and meet his oxygenation needs. This is what is known as Hyaline Membrane Syndrome or Newborn Respiratory Distress Syndrome. In this case, if the baby is not intubated and connected to Mechanical Ventilation, he will die by suffocation. There are other problems associated with prematurity that are related to gastrointestinal, neurological, ocular and infectious problems that are the product of organic immaturity and the methods used to sustain the life of these newborns.
To improve the evolution and prognosis of a Premature Newborn, Pulmonary Maturation and Brain Neuroprotection is indicated
What can I do to prevent premature birth?
- Regularly attend your gynecological consultation and share with your doctor your desire to “get pregnant”
- Start your Prenatal Control early when you know or suspect that you are pregnant
- Do not omit information regarding your health and illnesses when your Obstetrician performs the Medical History.
- Attend and follow the instructions of your doctor at each Prenatal Control visit.
- Do not make excessive or exhausting efforts.
- Eat properly and drink plenty of fluids during the day.
- Avoid sexual intercourse if they produce uterine contractions
- Avoid excessive stimulation of the nipples (this induces uterine contractions)
- Meets physical rest if your doctor told you so.
- Avoid exposing yourself to the risk factors mentioned: tobacco, alcohol, drugs.
- If you suffer from any disease do not neglect its treatment and control
- Establish a close contact with your doctor and report early any event or doubt you may have.
Early detection
Cervicovaginal Fetal Fibronectin 22-24 weeks
The measurement of this placental substance at levels higher than 50 ng / mL indicates a 25% risk of premature delivery before week 34.
Cervical length
This photo shows a cervix, long (> 25 mm) low risk for premature delivery. (Video)
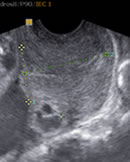
The measurement of the cervix less than 15 mm before week 24 implies a 30% risk of premature delivery before week 34 .
Since 2011, I have evaluated all pregnant patients to detect those that could be at risk for preterm birth by measuring the length of the cervix using transvaginal ultrasound between weeks 16-24 of pregnancy. I prefer to do it around week 24 to detect risk of preeclampsia using uterine artery Doppler and fetal health through Fetal Doppler to give a comprehensive judgment of some of the most frequent risk factors of pregnancy
A cervical length less than 25 mm. before week 24 (16-24), especially in the presence of other changes described in the medical literature, predict with a high safety value that delivery will occur before week 37, this avoids having to wait for a previous loss characteristic to make the diagnosis of Cervical Insufficiency
In women with necks of 20 mm or less during the evaluation of weeks 20-24, the start of labor is expected before 40 weeks in 95% of cases.
In women with necks of 30 mm or more during the evaluation of weeks 20-24 the start of labor is not expected before 40 weeks in 95% of cases.
This data allows us to closely monitor pregnancy and take appropriate measures such as limiting maternal activity, rest, fetal lung maturation and initiate, according to recent guidelines, the intravaginal use of Progesterone (200 mg at bedtime) during the rest of pregnancy (week 24 to 34) reduces the risk of premature birth by 45%.
Natural progesterone (intravaginal administration, 200 mg at bedtime from 24 to 34 weeks) in women with necks of 15 mm or less in the evaluation of 20-24 weeks reduces the risk of preterm birth before week 34 in 45%
And so it was, Roberto Romero, a researcher, published a paper where he established risk reduction using progesterone ( AJOG, 2017)
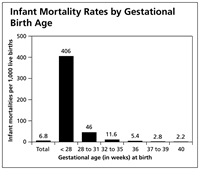
Mortality due to prematurity, cases per 1000 births.
The younger the gestational age, the greater the neonatal mortality.
Warning signs for premature birth
- Increased pelvic pressure, as if the baby was pushing down
- Sensation of intermittent pelvic heaviness
- Pain or pressure in the lower back, intermittent and different from the pain that already had if it were the case
- Loss of fluid from external genitalia
- Genital bleeding or expulsion of mucus with blood (mucous plug)
- Colic-like cramps that match the “hard belly”, painful uterine contractions
- If you are not sure of what is happening or you feel “strange” call your doctor
Prevention is fundamental in the reproductive health of women: every little effort we make for the health of our children will bring great and beautiful results
Cervical insufficiency
Formerly called Cervical Incompetence.
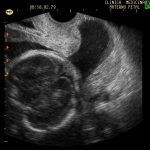
This photo shows a very particular situation: even when the neck measures 44 mm, the entire dilated trajectory (black tubular zone) is appreciated. Everything black is amniotic fluid and the rounded structure on the left corresponds to the baby’s head.
This condition is called Cervical Incompetence (associated ACOG literature, now it should be called Cervical Insufficiency) and it is a dilation of the cervix without pain that leads to a premature delivery around week 20 with a terrible fetal prognosis if you can not control the situation.
The treatment in this case is surgical and is based on knotting the neck with a loop of thick suture to avoid premature delivery: Cerclage of Uterine Neck.
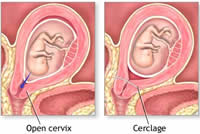
This procedure is performed around week 14 and the patient should maintain relative or more strict rest throughout the pregnancy.
If the patient starts labor, it is considered an emergency since the suture must be removed immediately to avoid bursting and hemorrhaging of the cervix. Many specialists plan a cesarean to avoid complications
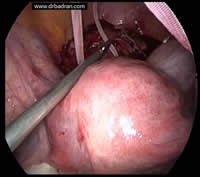
Preconception Cerclage is carried out intraabdominally by open or laparoscopic surgery in high-risk patients before a new pregnancy. It has the advantage of being more effective than the traditional one and can be left in situ for several pregnancies. It is a little known modality.
WHO recommendations on
interventions to improve
preterm birth outcomes