- Citas Centro Médico de Caracas: Lunes, Miercoles y Viernes. Pulse el botón Agende una Cita
- Sistema de citas en linea exclusivo para Centro Medico de Caracas en San Bernardino
- Citas CMDLT: Jueves. llamar al 0212-9496243 y 9496245
- Las Emergencias son atendidas en CMDLT previa coordinacion personal al 04142708338
- Proveedor Seguros Mercantil y Sudeban

The appearance of high blood pressure during pregnancy, in a previously normotensive woman, is called hypertension induced by pregnancy (PIH). Its most important forms are Preeclampsia and Eclampsia, treated in this article. Its milder form, the Gestational Hypertension, only includes occasional and slight elevations of blood pressure that yields with rest.
The workforce in Hypertension in Pregnancy of the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ACOG) made some changes in 2013 to unify the diagnosis and treatment of the condition. The intention is to decrease one of the most important complications of the disease, prematurity created by the termination of pregnancy before week 37; likewise, it is sought to reduce the indication of antihypertensive medication (medicating above 150/100: labetalol, methyldopa and nifedipine are the choice), avoid the use of magnesium sulfate in non-severe cases and avoid bed rest.
What does preeclampsia mean?
In a nutshell it means something that precedes or occurs before Eclampsia (Pre-Eclampsia). This is the occurrence, exclusively during pregnancy , of high blood pressure ( hypertension) in the presence of alterations in the kidneys ( proteinuria : excessive loss of protein through urine) and accumulation or “fluid retention” in the form of swelling or edema At present, ACOG does not consider the presence of proteinuria necessary to make the diagnosis of preeclampsia if other conditions are present
Preeclampsia is a disease that only occurs in pregnancy and pregnancy is the source, is one of the diseases that are part of the whole of the Hypertension Induced by Pregnancy (HIE), at the end of pregnancy the disease disappears and Preeclampsia can not exist if there is no pregnancy. This problem occurs in 2-7% of all healthy pregnant women and its frequency is much greater when the patient has some previous diseases, especially kidney. In the population of healthy women, preeclampsia is seen more frequently in first-time babies.
Gestosis, Gravidic Toxemia, Hypertension Induced by Pregnancy, what is its relationship with Preeclampsia?
They’re synonyms. Currently the most used is that of pre-eclampsia as one of the forms of hypertension induced by pregnancy
What is the origin of preeclampsia?
We do not know. But it is suspected that there is a defect in the way the placenta develops inside the maternal womb and this results in a series of vascular changes that lead to reversible damage to the kidneys ( Glomeruloendotheliosis ), elevation of maternal blood pressure, poor irrigation blood of the uterus and inadequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus in the medium term.
What are the symptoms?
An important part of the patients does not present any symptom. They are data of severity and / or complications the presence of visual disorders (scotoma scintillation), abdominal pain in the mouth of the stomach, significant swelling in the feet, hands and face; headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, decreased fetal movements, genital bleeding and seizures.
How is preeclampsia diagnosed?
The diagnosis is quite simple, but in order to do so, the patient is required to attend her Prenatal Control regularly, since in most cases Preeclampsia follows an asymptomatic course and is only discovered when performing routine arterial blood pressure measurements. When the symptomatology is intense, it usually suggests a severe problem with immediate possibilities of seizures (Eclampsia). The elements that we use to make the diagnosis are: Blood Pressure Equal or Greater than 140/90 mmHg with at least one additional criterion:
Criteria 2013, ACOG, Task Force on Hypertension in Pregnancy: Preeclampsia
- Blood pressure greater than or equal to 140/90 after week 20 with any of the following elements.
- Present proteinuria:
- > 300mg in 24 hours (one full day’s harvest) or
- Index Protein/Creatinine> 0.3, or
- Absent proteinuria: recent appearance of any of the following elements:
- Platelets less than 100,000
- Creatinine greater than 1.1 mg / dL (Renal insufficiency)
- Transaminases elevated to more than twice its normal upper value (SGPT, SGOT)
- Pulmonary edema without known cause
- Symptoms of the brain (headache) or typical visuals (scotomas)
Are there degrees of severity in this disease?
The traditional classification is based on blood pressure levels and deterioration of kidney function as well as neurological symptoms and the presence of seizures. In this way we have mild pre-eclampsia, severe pre-eclampsia and eclampsia, there is no moderate reeclampsa. The problem with this disease is that it can go from one degree to another without warning and even manifest a severe or complicated form of nothing and without having gone through milder forms. The greater the severity and early inio (very close to week 20), the greater potential for complications.
Criteria 2013, ACOG, Task Force on Hypertension in Pregnancy: Severe Preeclampsia
- Blood pressure greater than or equal to 160/110 plus any of the following
- Platelets less than 100,000 or
- Liver damage: elevated transaminases or unexplained epigastric pain / right hypochondrium that does not yield with usual treatments (antacids, common analgesics)
- Progressive renal failure
- Pulmonary edema
- Cerebral or visual symptoms of recent appearance
- HELLP syndrome (see box on the right, includes several elements)
Maternal complications
The most feared maternal complications are Eclampsia, acute liver damage (HELLP syndrome), acute pulmonary edema, renal failure, hemorrhage, stroke, coma and death. We also have to consider the personal and family impact of an emergency Caesarean section, of a possible admission to intensive care of adults, high costs and the psychological cost around the sick mother and her baby.
Fetal complications
The most feared risk is fetal death and the most frequent is prematurity, either because premature labor is initiated or because the pregnancy has to be interrupted due to the impossibility of controlling the disease. On the other hand, the placental disorder (placental insufficiency) leads to low birth weight babies and in some cases to neurological injury with important motor and intellectual sequelae.
Does prenatal care help?
Yes. Although it does not prevent it 100% (there are some strategies that could, but are inconclusive) or cure, you can establish the risk of each patient, diagnose the problem early, closely monitor the mother and her baby and control the situation in the best possible way. Good control has allowed a considerable decrease in neonatal mortality. The Doppler study of the Uterine Arteries allows to predict the appearance of HIE in asymptomatic women long before the appearance of high blood pressure figures.
Who is at risk for preeclampsia?
Although many times we do not know who will suffer, the following conditions put the patient at particular risk:
Firstlings (Primigestas), Family History or Personnel of Preeclampsia, Obesity (BMI> 30), Chronic Hypertension, Kidney Disease, Multiple Pregnancy, Diabetes Mellitus, Autoimmune Diseases, Low Socioeconomic Condition, Users of Cocaine, Amphetamines and others, In vitro Fertilization
I suffer from some of these diseases: Chronic Arterial Hypertension, Diabetes Mellitus or Chronic Kidney Disease. What should I do?
You must plan your next pregnancy in advance and attend Prenatal Control before you get pregnant: Preconception Control. You must keep your illness under control and you must tell your specialist doctor that you intend to become pregnant so that he can make the necessary adjustments, including the change of some contraindicated medications in pregnancy and if there is no contraindication for a pregnancy. Unfortunately, pregnancy can accelerate your pre-existing illness and lead to a considerable deterioration of your quality of life. In some cases we have seen the need to contraindicate a pregnancy or even have to interrupt it due to the accelerated deterioration of maternal health: in many of these cases the reason was the appearance of preeclampsia that damaged maternal vital organs or worsened the disease basic and endangered his life, there was no other option but to end the pregnancy. The good news is that this is quite rare but you should put a lot of your part in controlling your illness so that this does not happen.
Can it be prevented?
It is possible to minimize the number of cases and limit their adverse effects by changing some negative aspects in life habits, controlling chronic diseases and initiating adequate and early prenatal control, preferably before pregnancy . In the worst case we could at least detect it early and take stricter prenatal control measures to attenuate the maternalfetal consequences of the disease. The most recent studies ( Werner et al., American College ) indicate the use of aspirin much more widely and with an approximate reduction of 20% over the initial risk:
ASPIRIN 81 MG: 1 tablet daily during the whole pregnancy starting before week 16 (12 to 20) if you suffer ONE of these conditions:
- Chronic hypertension
- Multiple pregnancy
- Mellitus diabetes
- History of preeclampsia
- Renal disease
- Autoimmune disease
or
TWO or more of the following:
- Nulliparity
- Obesity (BMI> 30)
- More than 35 years
- Black race
- Family history of preeclampsia
- Last pregnancy more than 10 years ago
- Babies with growth restriction
( ASA Indications: Canadian Institutes for Health Research )
Some studies suggest that the use of Vitamin E and Vitamin C could prevent it in selected patients but the reports show a very variable effectiveness.
Can you predict?
Knowing the personal history of the patient we can suspect which of them will be more at risk of suffering from preeclampsia but there is no 100% sure prediction method, however, Doppler study of the maternal circulation (uterine arteries) can predict the appearance of preeclampsia up to 50% of patients with suspicious findings.
It can be cured?
Yes. But the only way to cure it is to interrupt the pregnancy . As with all diseases of unknown origin, the treatments are not effective and usually do not cure or eliminate the adverse condition. The only thing that we have clear up to now is that preeclampsia is cured by interrupting the pregnancy but as this is not always beneficial for the baby (due to prematurity) we must control the situation with medicines and general measures until we can extract the baby with some security.
I already had preeclampsia in my first pregnancy, will I suffer in the next?
In this case the risk of recurrence of the disease is increased; thus, you have an approximate risk of 20% of having Preeclampsia again (range 5-80%) depending on the severity of the previous episode and factors such as residual hypertension, diabetes, multiple pregnancy, etc.
If I swell, do I have preeclampsia?
Not necessarily, to make the diagnosis of Preeclampsia the swelling (edema) must be abnormal and be accompanied by hypertension and urinary protein loss. The inflammation of the ankles (edema) is normal in pregnancy, especially at the end of the day.
They tell me not to eat salt. Should I leave it?
No. That is an old and wrong conception to handle the problem. It does not improve the disease at all and could bring undesirable consequences. Keep the level of saline intake to which you are accustomed unless it is demonstrably excessive. If you consider that your intake is very high, discuss it with your doctor.
If I suffer from preeclampsia, do I have to be hospitalized?
In most mild cases, management can be outpatient and hospitalization is not indicated. In cases of severe preeclampsia the patient must be hospitalized and her pregnancy monitored closely; Many of these hospitalizations end in premature terminations of pregnancy to avoid complications of the breast and / or your baby. If Eclampsia is present, an emergency Caesarean section is practiced immediately almost universally.
Final recommendations
- Plan your pregnancy.
- Start a preconception care (this is the ideal pregnancy planning)
- Start an early prenatal checkup if you are already pregnant.
- If you suffer from a chronic illness, check it properly with a qualified specialist before starting a pregnancy.
Very deceiving
Severe hypertension (160/110 and older): 20-54%
Mild hypertension or normal tension (140-160 over 90-110): 30-60%
Edema and proteinuria
Severe: 48%
Without edema: 26%
Without proteinuria: 14%
Even though hypertension is the most important data for diagnosis, it may be absent in up to 16% of cases (in these cases there are other elements such as proteinuria, laboratory changes or typical symptoms), we are very careful in these cases and prefer to diagnose them as Preeclampsia and thus monitor them more closely).
Prediction
Personal factors: Black patients, personal or family history of preeclampsia, arterial hypertension.
Evaluation week 11-13: Maternal arterial pressure, uterine Doppler, serum measurement of PLGF and PAPP-A (not available in Venezuela)
This combined strategy detects 90% of cases of early preeclampsia (before 34 weeks) and 45% of late cases (> 34 weeks), we still do not do it
Evaluation week 24-28, Doppler : during the study of Third Trimester Risks we evaluated the uterine and classified the patient of low or high risk for preeclampsia.
We do it routinely and we have obtained excellent detection rates.
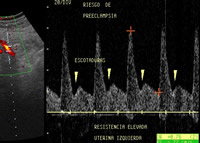
Uterine artery Doppler with risk markers for late preeclampsia. Pregnancy of 26 weeks. The patient was closely monitored and only manifested a mild form known as gestational hypertension
Laboratory: Measurement of proteins and creatinine in simple urine in the morning for calculation of the Pr/Cr Index
Normal: <0.15
Doubtful: 0.16 – 0.26.
Significant: 0.27 – 0.69
Definitive:> 0.7
In the ranges of 0.16 to 0.69 it is indicated to collect urine to measure proteinuria for 24 hours.
Hellp syndrome
It is a severe complication of preeclampsia and is characterized by profound and dangerous hematologic changes that can lead to massive maternal hemorrhage and multiple organ injury
The origin of Hellp syndrome (hemolysis, hepatic enzyme elevation, low platelets), severe complication of preeclampsia, is unknown.
The consensus is that the immediate interruption of pregnancy is accompanied by rapid recovery
Pregnancies under 24 weeks with HELLP are difficult to manage and are usually accompanied by fetal loss
Pregnancies of 24-34 weeks benefit from the use of inducers of fetal lung maturation (steroids) and sui allows it, a period of inpatient surveillance until the interruption is inevitable
In pregnancies after 35 weeks the indication is immediate interruption
- Most cases are seen during pregnancy, but some can manifest in the first 48 hours after birth.
- Pulmonary maturation with steroids is very beneficial at 24-34 weeks of pregnancy
- The steroids applied after week 35 have doubtful utility; however, according to the American College, they should be used if a cesarean section is performed before week 38.6
In our practice we do not do this because our rate of newborn respiratory distress (RDS) is almost nonexistent, perhaps because our demographics are different, especially regarding the daily diet and maternal body weight.