- Citas Centro Médico de Caracas: Lunes, Miercoles y Viernes. Pulse el botón Agende una Cita
- Sistema de citas en linea exclusivo para Centro Medico de Caracas en San Bernardino
- Citas CMDLT: Jueves. llamar al 0212-9496243 y 9496245
- Las Emergencias son atendidas en CMDLT previa coordinacion personal al 04142708338
- Proveedor Seguros Mercantil y Sudeban

Multiple pregnancy is the presence of more than one baby in the womb, it is a complication of pregnancy and although it occurs naturally it does not constitute a “normal” condition for the human being, the womb and the maternal organism are poorly prepared to give the necessary shelter to two or more fetuses simultaneously and this is demonstrated by the increase in complications that occur with this type of pregnancy. In fact, multiple pregnancy can be considered a little failure of fine reproductive controls in humans.
One of the most feared complications, aside from prematurity, is the Fetal Fetal Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS), which consists of abnormal communication of the placental circulation of both fetuses when sharing the same placenta (exclusive of the monochorionic twins). Both fetuses will be affected and eventually both will die if appropriate measures are not taken
Naturally we can say that 1 in 100 pregnancies will be multiple, but if we take into account treatments for infertility ( Assisted Reproduction ) we can see that they occur in about 20% of pregnancies achieved by basic measures (artificial insemination, Ovulation induction) or even greater if they are achieved through advanced techniques such as In Vitro Fertilization.
This article will basically talk about the double pregnancy known as twin pregnancy. The cases of high-order pregnancies (3 or more babies) present the same complications but with greater severity and frequency.
How is it produced?
There are 2 types of twin pregnancy: Dizygotic and Monozygotic.
Dizygotic : they represent 70% of the cases , they are known as Morochos (Fraternal Twins) and they occur when the woman has a double ovulation and each ovule is fertilized by a sperm, they can have the same or different sexes , they are genetically different even when physically they might seem. Each baby has its own placenta and its separate amniotic sac , there is a family tendency to repeat itself in subsequent pregnancies and generations through the mother’s side and suffer fewer complications and problems compared to its monozygotic counterpart. Obstetricians are reassured to know that the twins are of this type since the complications are minor and the management is simpler.
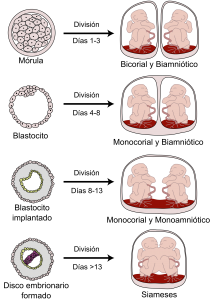
There is only one classification for this pregnancy: Bicorial (2 placentas) Biamniotic (two amniotic sacs) . This type of placentation can also be seen in early division monozygotes
Monozygotic: represent 30% of twin pregnancies . They are the product of the fertilization of an egg by a sperm but for reasons that are not clear the initial cell mass is divided into two groups before day 13 after fertilization and two babies are born genetically identical and of extraordinary resemblance (although sometimes they do not look alike), they occur randomly and have no hereditary relationship, babies can have separate placentas or a single placenta and can similarly have different amniotic sacs or share a single sack . In popular slang these are the real twins or twins (Identical Twins). The sexes are always identical . When they share placentas fetal problems increase and when they also share the same bag the problems can be made even more severe.
Classification identical twins:
- Bicorial Biamniotic (two placentas two bags, 30%) : same as the morochos. In this case they are identical twins from a single fertilized egg that was divided in the first 72 hours after fertilization. Excellent forecast
- Monocorial Biamniótico (a placenta two sacks, 65%) : the embryonic division occurs between day 4 and 8, this allows the embryo divided in two to separate completely but the placenta remains together. Babies each have their own sack but share the placenta. Complications occur frequently (20% risk of TTTS).
- Monocorial Monoamniotic (a placenta, a sac, 5%) : the division occurs between days 8 and 13, this only allows separation of the babies but they share the same sac and placenta. This is a rare event with high fetal mortality due to the fact that the babies can entangle their cords and die immediately at any moment or manifest vascular communications of the TTTS type (this is quite rare, maybe it does not give time to manifest)
- Monocorial Monoamniotic Siamese (one placenta, one bound sac, 5%) : after day 13 there is no time for embryo separation to occur and the babies are united to a greater or lesser degree by the thorax (thoracopagus), head (craniopagus), abdomen (omphalopagus), buttocks (ischiopagus), etc.
- Monocorial Monoamniotic Heteropago (one placenta one sac inside the other) : this is the rarest case that exists, it is a Siamese twin form where a baby or parts of a baby (almost no head) are inside another baby. Occurrence 1: 1,000,000. (Xie et al.)
What are the risk factors for having a multiple pregnancy?
Dizygotes:
- Maternal age, especially older than 35
- Black or Asian Race
- Multiparity
- Family history, especially in the mother’s line
- Ovulation induction, artificial insemination
Monozygotes:
- In vitro fertilization
- Chance, fortuitous event
How do you diagnose Multiple Pregnancy?
From 5-6 weeks the diagnosis of multiple pregnancy can be made using high resolution Ecosonography equipment via the Transvaginal route. This is the most sensitive method that exists. By week 10, it can already be determined if the fetuses share placentas or amniotic sacs.
Is multiple pregnancy a High Risk condition?
This is not an adequate condition for the human being. The presence of 2 or more babies, the presence of a large placental mass, uterine overdistension and more pronounced physiological changes increase the risks already existing in a simple pregnancy, up to six times the risk of complications associated with pregnancy.
Evanescent Twin: when we make the early diagnosis of a twin pregnancy (5-6 weeks) it is possible that in later studies only one fetus is observed. This is because in a significant fraction of these pregnancies one of the 2 embryos does not develop and is reabsorbed (in up to 60% of cases). Usually the survivor has no problems, it would be necessary to see if this is not a natural defense mechanism against a high-risk pregnancy instead of being a complication of multiple pregnancy.
Fetal death (> 10 weeks): intrauterine death is increased. When one of the two dies, the surviving fetus has more risk of dying than if it had been alone from the beginning. With different placentas the mortality can reach 14%, if the babies have a single placenta the mortality increases to 26% and if they also share the same amniotic sac the mortality of at least 1 baby can oscillate around 50%. Infant mortality in Simple pregnancies is 5/1000, Doubles 23/1000, Triples 52/1000 and Quadruples 96/1000.
Chromosomal risk and congenital malformations: due to their characteristics of particular origin (advanced maternal age) the risk of occurrence of chromosomal problems and anatomical anomalies is increased. Monozygotes have a chromosomal risk equal to simple pregnancy and the dizygotic risk doubled
Fetal-fetal transfusion (TTTS): if babies communicate their arterial and venous circulations, a baby will not grow as he passes his blood to his partner (donor) and the partner in turn will be overburdened (receiver) , will grow more than the other but eventually it can die as a result of physiological disorders. In addition, when one of them dies, the survivor can be affected by severe hypotension and the degradation products of the former. Fetal death occurs in 10% of cases before week 12 due to early onset of this condition. The risk of occurrence is 20%. I have had good and bad cases, luck and early diagnosis make the difference. The treatment is based on intrauterine fetal surgery with coagulation of interfetal vascular anastomosis
Decreased growth : if the placental conditions and perfusion of the maternal uterus are not adequate one or both babies may not grow properly and manifest signs of chronic fetal distress, the risk of low weight is 20% with separate placentas (bicorial) and of 30% when it is a single placenta (monochorionic). In general, twins are less heavy than babies of simple pregnancies and apart from that, one little brother can be quite smaller than the other (discordant growth). As of week 32, a considerable decrease in the rate of fetal growth in twins of double placenta (the most frequent) when compared to single fetuses is noted, it is striking that the growth of the fetal head is protected and can even be be greater in twins of this type pointing to a protective effect by nutrition / selective irrigation of the brain. The average weight of the twins in week 35 is approximately 2370 grams, 200 less than a single fetus in the same week
Placenta previa : because the extension of two placentas is greater it is possible that some of them occlude the orifice of the cervix producing genital bleeding and risk of prematurity due to emergency interruption before the end of pregnancy.
Prematurity : approximately 25% of babies born of multiple pregnancies are born before 37 weeks of pregnancy, the risk is greater in the monochorial. The average duration of a twin pregnancy is 35 weeks (premature). In addition to the indicated fetal complications, maternal complications such as Anemia, Preeclampsia and Gestational Diabetes are also present. It is clear that multiple pregnancy is a complication of human pregnancy.
Why is there more risk of prematurity?
Prematurity is a situation of high fetal risk expected in multiple pregnancies. There comes a point where the maternal womb is no longer able to maintain the volume composed of 2 placentas, amniotic fluid and 2 babies, uterine overdistention is a strong stimulus to generate uterine contractions that modify the cervix. The maternal-fetal circulation (Uterus-Placenta) may be insufficient to meet the growth needs of fetuses and if, in addition, we add to these factors the increased incidence of anemia, pre-eclampsia and diabetes we will have many ingredients that can give rise to a Preterm Labor that ends the pregnancy in the presence of small and immature babies. Pulmonary maturation in twins who will be forced to be born between weeks 24 and 34 improves the prognosis of neonates.
Why do babies have different weights?
The variation in weight may be due to differences in the function of each placenta and the amount of blood that comes from the mother each one touches. The best irrigated and efficient function placentas will keep babies better nourished and therefore of better growth.
How is the prenatal control of a twin pregnancy?
It must be stricter and more frequent, nutrition must be adjusted very well (this is extremely important), physical exercise and working hours. It must include a lot of rest and suspend professional or domestic tasks early. In many cases the woman goes to bed rest in the last weeks of her pregnancy, the twin pregnancy requires a lot of patience on the part of the patient. As obstetricians we must be very attentive to determine early the appearance of the usual complications, perhaps the most important of all is to advance measures against the possibility of a premature birth and prevention of preeclampsia.
What are the maternal changes?
In multiple pregnancy, the usual changes in pregnancy are even more exalted, hormone levels are much higher, nausea and vomiting are more intense, changes in respiratory function, cardiovascular, renal and endocrinological are more intense, nutritional needs they increase and the increase in body weight can be considerable. Functional body changes combined with weight gain, fluid retention (swelling) and a large abdominal volume print more work to the joint and muscle, heart and respiratory systems. All these changes result in increased fatigue, fatigue, respiratory discomfort, dyspnea, insomnia, heartburn, swelling, varicose veins, joint discomfort, etc.
How will my diet and weight vary?
It is expected that during pregnancy a woman will consume more calories daily (around 300 more) maintaining a balanced diet, will require more iron and folic acid and should consume calcium and multivitamin preparations early. All this means that the weight gain during these pregnancies is greater than what you would get in a simple pregnancy, the range ranges from 16 to 20 kilograms. Apparently the use of polyunsaturated oils, Omega 3, has beneficial effects with respect to the final fetal weight and the prevention of preterm birth
Can I give birth vaginally?
The mortality of a baby is 1 in 1000 in a simple delivery. In twin vaginal delivery, the mortality rate of the first child is 1% and that of the second child is 5.4%; this without counting the neurological sequels that may occur.
With this statistic, very few doctors will allow delivery vaginally. I, in particular, always do cesareans in these cases and despite that it is still a bit stressful, especially the extraction of the second baby. The final decision will be made by you and your doctor. In North America and Europe they report considerable numbers of vaginal births in this type of pregnancy.
At what time is the pregnancy interrupted?
According to the guidelines of the NHI (National Health Institute, Royal College of Obstetricians Gynecologists, page 157) the termination of pregnancy should be offered from the following weeks:
Triple pregnancy : 35.0 weeks . Usually requires use of lung maturation
Double pregnancy Monocorial : 36.0 weeks . Usually requires use of lung maturation
Pregnancies double Bicorial : 37.0 weeks . Does not necessarily require lung maturation
How will my daily life change?
You must assume your pregnancy very calmly, avoid strenuous work and exercises, rest regularly, assist without fail all your obstetric checks and tell your obstetrician any unusual symptoms. The diet must be healthy, balanced and you must be well hydrated at all times. Sexuality will be interrupted shortly after the beginning of the third trimester of pregnancy and intense physical exercise will be limited and eventually suspended. You will start the prenatal rest before week 34 and then you will spend most of the day sitting or lying down.
In general, if you start your Prenatal Control in early stages and follow the instructions of your Obstetrician, the chances of success and a happy ending are on your side; the current evidence establishes very clearly that a frequent and effective prenatal control, adequate nutrition, the suspension of smoking and alcohol, the reduction of emotional stress, frequent rest and close fetal control lead to better results than those obtained in multiple pregnancies Inadequately managed, in fact, they report a decrease of approximately 50% in all associated complications.
Placentation Identical Twins
I want morochos, what do I do?
The best you can do is to pray to God not to give you morochos, multiple pregnancy has many complications.
What if my ovaries stimulate me?
The obstetrician who induces ovulation, in the absence of infertility, only to comply with the whim of the patient to have morochos is incurring medical malpractice since multiple pregnancy can endanger the life of the mother and there is no sense in risking the patient .
With in vitro fertilization can we know the sex of the embryos before implanting them?
If you can but that brings an ethical problem: we have 5 embryos, 3 feminine and 2 masculine; you want the 2 men and they implant you; you have morochos at last, your wish fulfilled!
And the female embryos? freezes, boots or gifts?
In many countries the diagnosis of preimplantation sex is not allowed.
Infertility and multiple pregnancy
Assisted reproduction procedures greatly increase the risk of multiple pregnancy. Couples who get their babies after many frustrations are not at all aware of the sex of the babies; they are just people grateful to have lived the miracle of being parents without the egocentric whims.
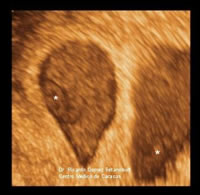
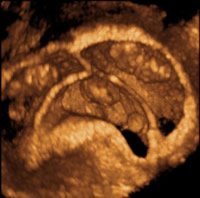
Twin pregnancy of 6 weeks, 3D image: 2 different and separate sacs are seen: dizygotic. The 2 embryos are denoted by asterisks. This pregnancy reached the end (week 38) without complications. A healthy male and female. Had it been of the same sex, it would have been possible to be monozygotic.
The previous case in traditional 2D image.
High Order Pregnancy (3 or more): Triplets. In the image, the 3 gestational sacs and the 3 embryos are clearly visible. This pregnancy ended prematurely (week 31, the standard is 30, we won a week) due to maternal complications; However, the 3 babies evolved very well, their weights were 900, 1050 and 1300 grams.
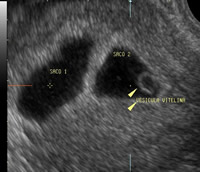
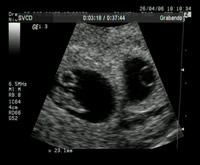
Evanescent Twin: Multiple double pregnancy of 8 weeks with evanescent embryo syndrome: note one of the bags with a visible embryo and another without an embryo. This occurs in 21-30% (or more if multiple pregnancy is diagnosed early, around week 6) of double pregnancies and usually does not pose problems for the other baby. The residual bag will be absorbed without inconvenience. The rounded hollow structure is the vitelline vesicle and the white cylinder is the embryonic mass.
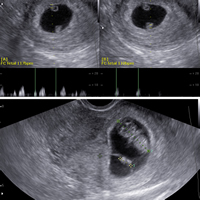
In this case the embryos shared the same placenta. Up week 6 and down week 9. The lower embryo did not develop.
Siamese
If the division of the embryonic mass is delayed, there is no time for the embryos to separate, so they remain united, sharing organs in a variable and complex manner.
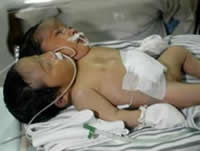
Siamese twins born in Indonesia on July 23, 2009. These babies have a single body maintaining independence in hearts and heads.
Case of the Hensel Twins. USES
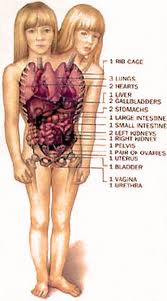
At the age of 20 (March 7, 1990), they are Siamese twins who share all the organs below the navel. They are intellectually independent, and they already have a license to drive vehicles. They are lucky to have been born in a developed country.

This is the body relationship