- Citas Centro Médico de Caracas: Lunes, Miercoles y Viernes. Pulse el botón Agende una Cita
- Sistema de citas en linea exclusivo para Centro Medico de Caracas en San Bernardino
- Citas CMDLT: Jueves. llamar al 0212-9496243 y 9496245
- Las Emergencias son atendidas en CMDLT previa coordinacion personal al 04142708338
- Proveedor Seguros Mercantil y Sudeban

Most obstetricians have always been very jealous about physical exercise during pregnancy; however, recent evidence has shown that in the absence of obstetric complications or high-risk pregnancies moderate to intense exercise not only has excellent benefits for the mother but also for her baby. We have always been very cautious with the effects that exercise (through the increase of body temperature, the release of stress hormones, caloric expenditure, the “theft” of blood to the uterus, etc.) could have on pregnancy but fortunately the evidence suggests that these mechanisms are not a problem for the mother or the fetus. In a few words it seems that we have been very alarming in what refers to exercise during pregnancy. Current knowledge has allowed us to be more liberal and allow higher levels of activity than we previously allowed.
I was struck by the fact that exercise, far from being harmful to the baby, has shown not only immediate benefits for the fetus but also delayed and evident in the newborn, benefits that extend beyond childhood. Do not miss the exercise in your pregnancy! It can be more effective than all the vitamins that we indicate …
Data to know in an easy and practical way if you are exceeding with the exercise : if you can not keep a fluent conversation during the exercise, because you lack the air, you must slow down!
Warning: we are supposed to be talking about uncomplicated pregnancies, if you have any questions ask your doctor.
Categories
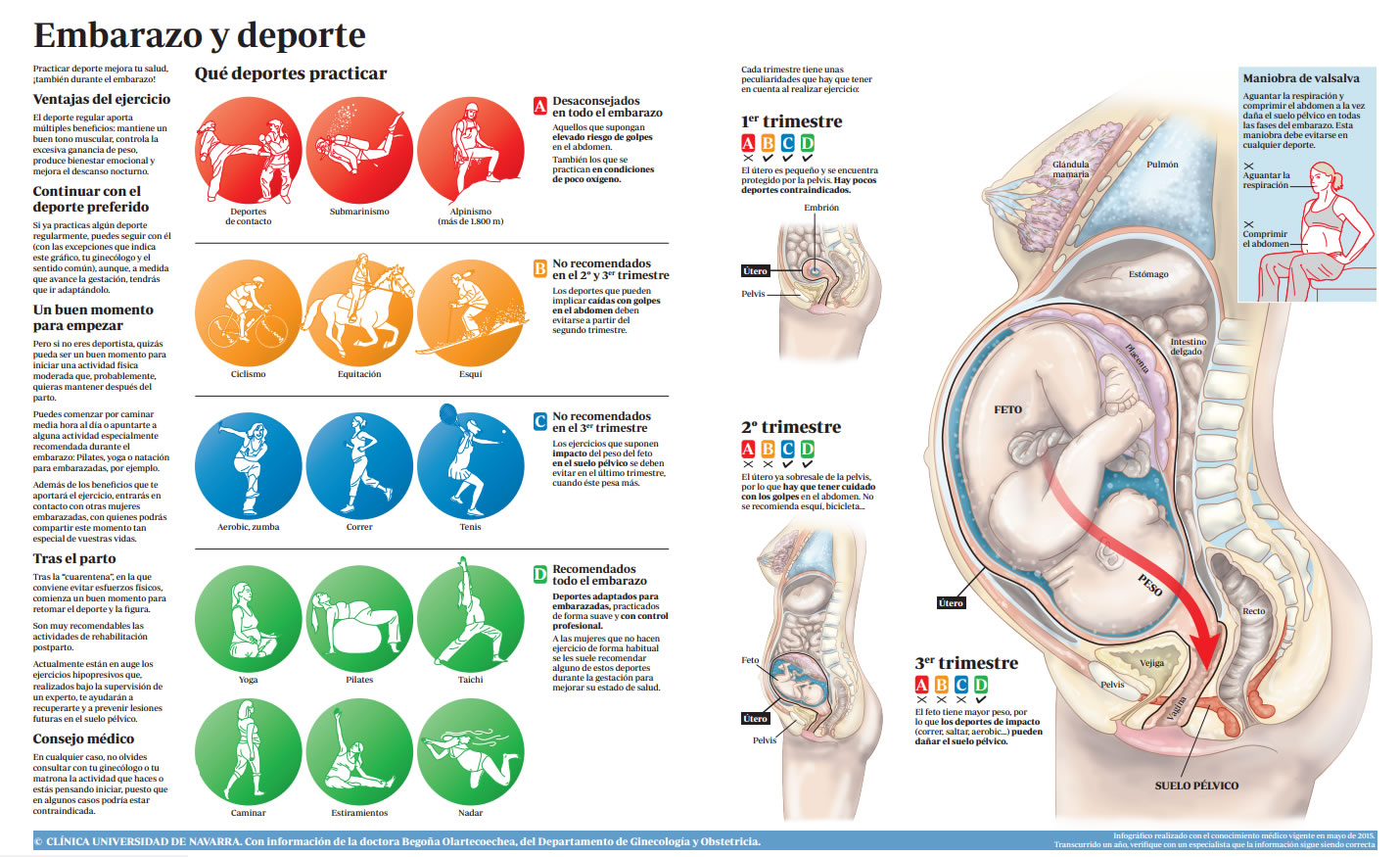
Logically, all the exercises are not the same, nor are the great variations in intensity, duration and frequency of the studied regimens and the particular period of pregnancy in which the phenomenon was studied, which is why the information has been confused. over the last 3 decades. The ACOG guidelines have passed the test of time and as more women are exercised we have better information so that we can be a little more permissive.
Untrained women
In this group are the majority of pregnant women and is the main objective of my article: to stimulate with evidence sedentary women to begin to exercise. Although I am a regular visitor of gym and outdoor sports, I must accept that never, as now, I had given so much importance to physical exercise during pregnancy, as I mentioned earlier, it seems that physical exercise is better than many of the vitamins that we indicate during pregnancy, I do not mean that you leave them, what I want is that you start doing some exercise.
Moderate exercise in standing (walking, elliptical, steps, treadmills) is recommended for sedentary women who want to start in these areas, is based on exercise, from week 8 of pregnancy, 3 to 5 times per week in sessions of 20 minutes and working at 55-60% of the total aerobic capacity . The latter refers to exercising at heart rate levels equivalent to 55-60% of the maximum frequency allowed by sex and age; In any case, it is never recommended to reach heart rates greater than 160 beats per minute.
The good news: it was shown that women who trained in this way had larger placentas with babies of better weight than controls, this suggests a preventive role of exercise for intrauterine growth retardation due to placental insufficiency.
Women trained
Women who had and follow their previous exercise routine during pregnancy may continue to do so at the level they were used to but should always keep in mind that exhaustion, dehydration, body temperature elevations above 39 ° C, exercises are not recommended. high impact and those that are considered risky, over time it is inevitable that intensity decreases due to abdominal volume and physiological changes and discomfort of advanced pregnancy. Always exercise common sense! the extremes have never been good
We consider high volume exercises those performed with a frequency equal to or greater than 5 times per week in sessions of up to 1 hour and working above 55% of the total aerobic capacity. Remember that a trained person has lower resting heart rates and their cardiac response is lower than that of sedentary people, support more exercise with fewer changes. One of the most notable findings was that their babies were less heavy than controls but maintaining the body and psychomotor benefits in the first 5 years of life. This data can be useful to control the growth of babies of mothers who manifest Gestational Diabetes during pregnancy
The most interesting thing about exercise during pregnancy is that it not only brings benefits to the mother but also brings some important to the baby in the short, medium and long term. This seems simply marvelous and inexcusable: every mother should make the effort to give her baby any small detail that contributes to make her healthier, stronger and happier, than a great demonstration of love towards her unborn child and successful man or woman that one day will be!
Women Elite, the Professional Athlete: considerations of the International Olympic Committee (IOC)
Women who exercise professionally and high performance athletes are exposed to a wide range of physiological and potentially adverse effects during pregnancy, which incidentally, coincides with the period of better physical performance in their careers, 23 to 32 years . Eventually uterine dimensions, multiple organ physiological changes, fetal weight and the proximity of the birth of the baby will lead to the total suspension of professional activity to make way for motherhood and breastfeeding and upbringing for a time determined by the needs of the patient. Many athletes have abandoned professional training by week 20 to give way to less intense physical activity.
Fertility: It is suggested to start procreation at age 23 if you plan to have 3 children, at 27 if you plan 2 and at 32 if you plan to have one. Fertility may be diminished due to the effects of the Relative Energy Deficiency Syndrome in Sports (RED-S: energy expenditure is greater than intake and, together with the stress of intense exercise, menstrual, immunological, density disorders are observed bone mineral, protein synthesis, hormonal balance and other cardiovascular health).
Medications: prenatal medications are not prohibited by the IOC, are legal in anti-doping tests (including anti-emetics)
Eating disorders: they are more frequent in the elite population than in the general population (20-42% vs 3-9%, respectively). For this group of patients, maternal complications in pregnancy are much more frequent: hyperemesis gravidarum, anemia, abortions, preterm delivery, preeclampsia, caesarean section, and postpartum depression. For the fetus and the future development of the baby are also dangerous: low birth weight, congenital anomalies, anxiety, depression and use of illicit substances.
Musculoskeletal modifications: progressive uterine growth (and breasts) moves the center of gravity forward so that postural changes are given to re-establish balance. There are positional changes in the spine, shoulders, pelvis, knees and joints that have a negative impact on certain athletic specialties. The steps are shorter and the balance can be compromised, increasing the risk of falling. The speed decreases.
Cardiorespiratory and metabolic modifications: During pregnancy, the body temperature increases, there is greater cardiac work (higher heart rate and cardiac output) and greater pulmonary ventilation. There is a tendency for postural hypotension and dyspnea. Exercise tolerance and sports performance are progressively reduced as we approach the end of pregnancy. Hydration should be strictly monitored and the body temperature should not exceed 38.5 degrees C
Energy consumption: Increases progressively due to the requirements of the fetus, placenta and physiological changes, especially cardiorespiratory and thermometabolic. During the first quarter, an extra 90 Kcal / day is required, in the second 287 and in the third 466.
Exercise menu
Swimming : it is perhaps one of the safest activities since the floating weightlessness status does not print joint overloads, the body temperature is maintained at safe levels, the possibilities of injuries are practically nil and practically all the muscular groups of the body are used. The most important problem is the lack of availability of places to do it for most pregnant women
Fixed bicycle : this is one of the most studied exercises during pregnancy. It is taken as one of the safest and therefore recommended
Spinning : spinning is a competitive, more intense and structured variant of the stationary bicycle, in a study of 50 pregnant women who practiced Spinning 3 to 5 times a week and reaching heart rates of 150-160 there were no adverse effects. My recommendation: avoid extreme exhaustion and hydrate continuously during the session. In early stages of pregnancy, before week 10, it is imperative to avoid high body temperatures. In some places they play music so loud that it is not known if it disturbs the baby
Walking : This represents the most used form of exercise during pregnancy, it is “natural” and available to everyone. In the studies conducted there have been no adverse effects.
Jogging : it is the second exercise in frequency of practice during pregnancy; however, proportionally much below the traditional walk. Many women complain of breast pain, pubic or lumbar pain and joint in knees or ankles. Many women change to walk to avoid discomfort. If your previous physical training allows you to jog without discomfort because you will not have any problem as long as you follow the safety criteria in terms of temperature, hydration, exhaustion, etc. Buy shoes of good quality and adequate breast support.
Weightlifting : in a few studies there were no problems related to pregnancy, however I do not have data related to weights, routines or technical capacity of the coach in charge of supervision. My recommendation: use low weights, do not overload your back, avoid routines that increase intra-abdominal pressure, hydrate continuously and try to follow the instructions of a suitable trainer
Diving : Occupational divers have a higher frequency of abortions, premature birth and low birth weight fetuses (intrauterine growth retardation). Occasional diving above 10 meters does not seem to cause problems, but considering it as exercise (infrequent, not very aerobic) there is little benefit to maternal-fetal health. My opinion: a shallow dive on a cruise or tourist event (snorkeling) is not dangerous and is extremely relaxing
Yoga: it is on the rise as a form of exercise, however there is no demonstrable medical information that suggests maternal-fetal benefits. Although the mother can feel very well we do not know if the fetus benefits from such activity. Under some conditions the positions of yoga could alter the precarious joint balance that pregnancy exerts on the joints and generate pain in some of them. Prudence is recommended and perhaps only for those patients who already have sufficient previous experience with yoga.
Benefits for the baby
- Better fetal tolerance to a variety of important stressors before and during delivery: lower risk of fetal distress.
- Less amount of subcutaneous fat tissue at least until 5 years (the follow-ups were up to 5 years, we are waiting for the results of the studies until adolescence). This implies the potential to reduce the risk of Diabetes and Heart Disease, among other diseases.
- Better psychomotor development at birth and during the first 5 years of life.
- Adults potentially healthier in the long term, away from obesity, drugs, and other harmful excesses.
Maternal benefits
- Better physical and cardiorespiratory conditions during and after pregnancy.
- Weight gain controlled during pregnancy and easier to lower during the postpartum period and breastfeeding.
- Improvement in self-esteem and the feeling of feeling good, control of stress, less concern for the aesthetic changes of pregnancy, muscle toning and slimmer figure.
- Less joint discomfort and better musculoskeletal stability.
- Shorter and effective labor.
- Fastest postpartum recovery.
- Education and example for the whole family in the face of the need to maintain good physical and health conditions; elimination of negative habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol and nutritional learning; character development and awareness of the benefits of personal discipline, effort and perseverance.
Fast guide (in spanish)
Maruxa
Gently she lent us her pregnancy to show us that pregnant women enjoy exercise and its benefits.
Cardio

Machines: supervision, his trainer Roberto Rodriguez (Strucktura Gym, La Boyera, Caracas)

and weights …

By setting the example, you promote healthy attitudes in your family!
Guidelines and data
Modified guidelines of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG 1994)
Physical exercise is recommended for all healthy pregnant women due to its favorable effects on the cardiovascular, metabolic and biomechanical system
3 or more sessions of exercise per week are suggested, trying to make sure that its intensity does not reach fatigue or generate discomfort. Previously trained women can do more intense exercises than a beginner would be allowed
For safety reasons, during the exercise sessions the woman must pay special attention to the intensity and duration of her activity, taking care of the environmental conditions (temperature and humidity), hydration status and caloric intake before and after training.
Each session must be preceded by a period of warm-up and stretching and followed by a period of quiet cooling and relaxation
The chosen exercises must be safe and limit the risk of accidents. For example, mountain biking is not advisable given that the risk of trauma is relatively high. Choose swimming, stationary cycling (including spinning), walking or jogging in safe environments, for example
The complications of pregnancy or the presence of chronic diseases during pregnancy are contraindications to exercise.
Some clinical data …
Standing exercises (walking, jogging) are safe and are recommended to sedentary women starting at week 8.
Previously trained women can do this type of exercise up to 5 times a week, reaching moderate levels of intensity for up to one hour.
Moderate exercise during the early stages of pregnancy stimulates placental growth (better placenta, better fetal nutrition and growth)
The amount of exercise in the late stages of pregnancy has a significant effect on the baby’s weight at birth: intense exercise after week 20 decreases the baby’s birth weight due to lower fat deposits. Intense exercise should be accompanied by an increased caloric intake.
The 5-year follow-up of children of women who exercised during pregnancy demonstrated benefits in neurological development (behavior and motor skills) and anthropomorphic (body measurements).
The family example in health removes your cigarettes and alcohol from drugs, in addition to reinforcing appropriate and disciplined behaviors.