- Citas Centro Médico de Caracas: Lunes, Miercoles y Viernes. Pulse el botón Agende una Cita
- Sistema de citas en linea exclusivo para Centro Medico de Caracas en San Bernardino
- Citas CMDLT: Jueves. llamar al 0212-9496243 y 9496245
- Las Emergencias son atendidas en CMDLT previa coordinacion personal al 04142708338
- Proveedor Seguros Mercantil y Sudeban
Ectopic pregnancy (EE) is the abnormal implantation ( ectopic , out of place) of the embryo outside the maternal womb. Since the uterus is the only structure designed for the growth of the baby, any other location will not generate anything other than the loss of pregnancy and endangering the mother’s death. As we will see later, the only way to treat this problem is to interrupt the pregnancy either by Surgical methods (98%) or Physicians (<2%). It is not considered an abortion since its location is abnormal and therefore its presence and the treatment it generates does not contradict moral or religious factors. On the other hand, signs of life are rarely observed in an ectopically located embryo. This is a true emergency whose omission or diagnostic failure often leads to maternal death if not intervened in time.
Considerations
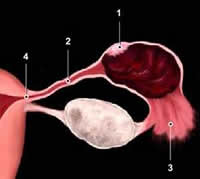
In more than 90% of cases the ectopic pregnancy is located in one of the fallopian tubes and in the remaining 10% can be seen in the uterine horn (junction of the fallopian tube with the uterus), over the ovary, in the abdominal cavity (Abdominal Pregnancy) and the cervix. When the pregnancy begins to grow in the wrong place, sooner or later it injures the tissue that lodges it and generates a potentially fatal internal bleeding for the mother, so there is abdominal pain, bleeding, signs of internal bleeding and absence of intrauterine pregnancy
The frequency described is 0.5-2%, the truth is that there has been a remarkable increase in the last 30 years in response to the Sexual Revolution of women since the 70s, the early onset of sexuality, multiple sexual partners (both male and female), endometriosis and the increasing prevalence of Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Despite having increased the number of cases, mortality has decreased by more than 90%, this paradox is due to the fact that the diagnosis and its treatment are more precise, safe and precocious at present.
How does it manifest?
Ectopic Pregnancy should be suspected in all sexually active women, using or not using any contraceptive method, to consult for pelvic pain, menstrual delay, symptoms of pregnancy (nausea, vomiting, breast tenderness), bleeding or genital spotting, and signs of internal or occult bleeding ( Ectopic Pregnancy Break).
How is it diagnosed?
The progress and availability of better methods has allowed the correct and early diagnosis of EE with a sensitivity greater than 90%.
With the current methods we can make the diagnosis before the deadly situation for the mother is presented, for this it is necessary that every patient that suspects pregnancy to practice a sensitive test and start prenatal control early. The methods that definitively changed the vision of ectopic pregnancy management were the appearance of sensitive pregnancy tests (it detects pregnancy even before the menstrual failure occurs ) and the high resolution Transvaginal Ultrasound ( USTV ). When a patient consults on suspicion of pregnancy, the first thing indicated is to perform a pregnancy test ( b- hCG) and a Transvaginal Ultrasound is performed to establish the anatomic location of the pregnancy, if there is one. In this way, early prenatal control discards early the presence of an Ectopic. If an intrauterine pregnancy is not detected in the presence of positive b- hCG, its presence should be suspected and, consequently, a diagnostic protocol should be initiated (serial measurement of the quantitative b- hCG every 72 hours) than in the course of 7 to 10 days ( must discard or corroborate their presence. When obtaining values ??of 3500 mUI / mL or greater (ACOG, Practice Bulletin 193, 2018), an EE should be considered and the termination of pregnancy indicated.
What are its complications?
The most feared complication is maternal death due to internal hemorrhage due to rupture of the organ where the egg was implanted. Other complications are those related to surgery, anesthesia and the use of drugs with potential toxicity.
Treatment
Immediate interruption!
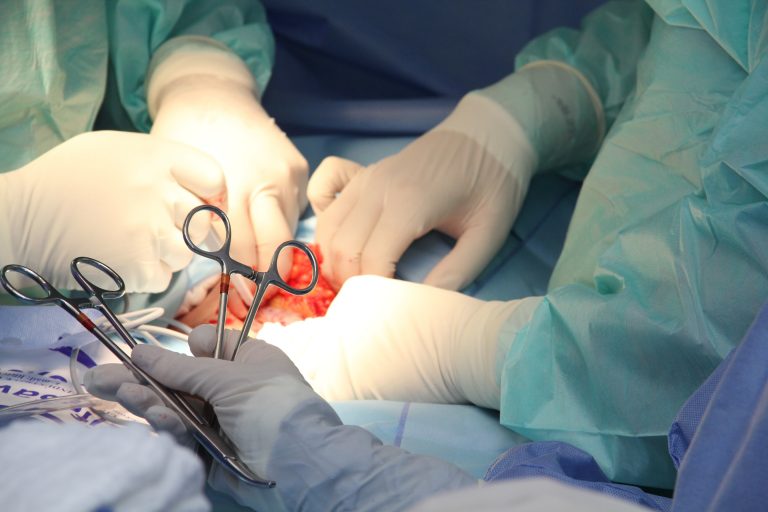
Surgery: In more than 98% of cases, surgery is the treatment of choice, either openly (traditional surgery) or through the use of laparoscopy, if the case allows. Usually the total removal of the affected trunk containing the pregnancy is required, but occasionally the uterus must be completely removed because of extensive lesions. Laparoscopic surgery and mini-laparotomy are the methods of choice for the treatment of ectopic pregnancy , limit surgical time and allow a very rapid recovery without adding more injuries to the female pelvis.
Medical Treatment: If the diagnosis is made early, a non-surgical treatment based on the maternal injection of drugs (methotrexate) that eliminate pregnancy in its early stages could be used. Unfortunately, many times the conditions are not given or the diagnosis is delayed, therefore only less than 2% of affected patients benefit from this option. In addition, this treatment has an effectiveness of 59-88% which depends on the time of pregnancy (the shorter the time the more effective). I practice it in a very small number of cases because the patient requires multiple evaluations and procedures that can be cumbersome and expensive, delaying, in many cases, the definitive surgical treatment
What are the sequels?
After a well-managed ectopic sequelae are practically nonexistent, however, the antecedent increases the risk of its recurrence in the future. Pelvic surgery is in itself a risk factor for the appearance of a new event. Chronic pelvic pain and discomfort related to surgery may occur. Even future fertility could be compromised due to injury caused by the pregnancy and the type of treatment performed.
How to prevent it?
The best prevention is to avoid pelvic infections (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease) and Sexually Transmitted Diseases, for this it is necessary to be Sexually Responsible: have a stable sexual partner, avoid promiscuity and use condoms during casual contacts. Not all cases can be prevented but Safe Sex prevents an important part. The early initiation of Prenatal Control discards its presence early, this is the best option since it would allow access to non-surgical or minimally invasive therapeutic options in the unfortunate event of an EE.
Can it be repeated?
Yes, probably the causes that led to an EE are still present at the time of a new pregnancy. Although the risk is present (and high) the chances of recurrence are lower than those of having a normal pregnancy: expect a normal pregnancy between 52-94% of cases
I had an ectopic in the past, what should I do?
If you had an Ectopic Pregnancy you should plan your future pregnancies and start a Preconception Control (prior to pregnancy). In this way, you can discuss all your concerns with your doctor and follow the instructions that you make earlier. At the first suspicion of pregnancy you will communicate with him and the relevant tests will be done to determine your location. Most women will have a normal pregnancy.
Causes
Although there is a wide variety of conditions that are associated with EE the most common cause is the direct or indirect injury of the Fallopian tubes that delays or obstructs the passage of the fertilized egg to the uterus in such a way that an implantation occurs outside the cavity uterine Let’s see the most important risk factors:
- Injury and tubal scarring due to pelvic infections, peritonitis, appendicitis
- Previous pelvic surgery including ovaries, tubes and appendix
- Congenital anomalies of the uterus or fallopian tubes
- Previous Ectopic Pregnancy
- Pelvic endometriosis
- Pelvic tumors that affect tubal function
- Intrauterine devices (IUD)
85% of patients who have had a previous ectopic pregnancy may have a normal intrauterine pregnancy in the future.
Frequent anatomical location
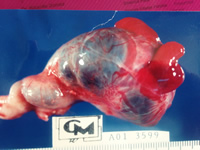
Real image of a tubal ectopic resected before rupture, 9 weeks pregnancy. The patient consulted for pelvic pain and menstrual absence.
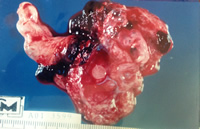
Open anatomical piece demonstrating the presence of a 9-week embryo in the upper right pole of the fallopian tube.
Images courtesy Dr Jesús E Iturriza. Medical Center of Caracas
Video of ectopic pregnancy in a fallopian tube. Observe the cardiac activity of the embryo.
Important
Ectopic pregnancy is not considered an abortion since its location is anomalous. There is no contraindication, moral, religious or legal for immediate interruption.