- Citas Centro Médico de Caracas: Lunes, Miercoles y Viernes. Pulse el botón Agende una Cita
- Sistema de citas en linea exclusivo para Centro Medico de Caracas en San Bernardino
- Citas CMDLT: Jueves. llamar al 0212-9496243 y 9496245
- Las Emergencias son atendidas en CMDLT previa coordinacion personal al 04142708338
- Proveedor Seguros Mercantil y Sudeban

Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted bacterium that affects the genital anus area in both sexes, approximately 50-70% of infections are asymptomatic but potentially harmful to the female reproductive system and the same in the male.
In the woman it causes urethral infection (Urethritis), inflammation of the cervix with production of purulent mucus (Cervicitis), uterine cavity (Endometritis), infection of the Fallopian Tubes (Salpingitis) and collections of pus in the tubes (Tubal abscess ), ovaries and pelvic cavity, a condition that as a whole is called Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) and whose medical importance lies in being a generator of infertility and death in women of reproductive age. As it is considered that around 5% of sexually active women are carriers of the bacteria it is possible to find chlamydia in the female reproductive system during pregnancy (2-37% of pregnant women).
Abortion or early pregnancy loss
Chlamydia has been inconsistently involved with abortions or early pregnancy losses but the results are contradictory because chlamydia is regularly associated with other bacteria, Mycoplasma and Ureaplasma, organisms that apparently have the greatest potential to produce abortions; In any case, we consider its presence as a potentially problematic factor. If we determine its presence in the female genital tract during the first consultations of the prenatal control, appropriate antibiotic treatment is indicated.
Complications of advanced pregnancy
The presence of chlamydia in the female genital tract after the first half of pregnancy (after week 20) ??has been shown to be a causal, but inconsistent, factor of preterm birth, intrauterine fetal growth retardation, low birth weight, premature rupture of membranes (RPM) and neonatal prematurity.
Labor and puerperium (postpartum period)
The passage of bacteria into the uterine cavity can cause a severe maternal infection known as puerperal endometritis; Likewise, the infection can affect the wounds practiced during childbirth or caesarean section giving rise to infections of the operative wounds that would delay the discharge of the patient from the hospital or could even make her come back for intensive treatment.
Baby infection
During delivery, the baby who comes in contact with chlamydia can suffer serious infectious complications, especially ocular or pulmonary:
Conjunctivitis : the neonatal eye contamination by chlamydia produces a condition called Conjunctivitis of Inclusion of the newborn. The baby begins to manifest abundant tearing that eventually becomes purulent, the eyelids swell and the eyes redden. Although severe ocular complications rarely arise, the disease is sufficiently bothersome for the baby to make him irritable, alter his diet and sleep.
Pneumonia : for a couple of decades it was discovered that chlamydia could cause lung infection or pneumonia. This if represents a serious and dangerous neonatal complication that occurs between weeks 4 and 11 (especially after 8 weeks) after birth. The baby begins to manifest discrete fever, nasal congestion, shortness of breath, cough, irritability and difficulty feeding and sleeping. It is a serious condition that requires immediate hospitalization and antibiotic treatment.
What can you do?
As many women are asymptomatic, the best remedy is to initiate prenatal care early and ask the obstetrician to take appropriate samples for the culture and detection of Chlamydia trachomatis.
- If the culture or test is positive your obstetrician will indicate appropriate antibiotic treatment to the couple
- Discusses the issues of fidelity and mutual monogamy to prevent the acquisition and transmission of sexual contact diseases (this is fundamental throughout life)
- If you are pregnant avoid sexual contact with unknown partners; if unavoidable, it is convenient to use condoms
Chlamydia and other
Chlamydia trachomatis is a germ of intracellular life, slow growth and with great destructive potential for the internal female genital treatment (uterus and fallopian tubes). In half of the cases, the patient has no symptoms and is totally unaware of their presence.
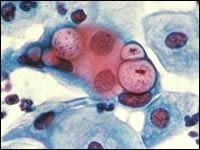
During pregnancy, we culture the cervix to detect its presence along with other potentially dangerous pathogens for the baby: Neisseria gonorrhea , Ureaplasma urealyticum and Mycoplasma hominis.
These bacteria have been implicated in Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Salpingitis, Endometritis, infertility, abortions, premature birth and neonatal infection. Upward infection during pregnancy can severely affect the baby.