- Citas Centro Médico de Caracas: Lunes, Miercoles y Viernes. Pulse el botón Agende una Cita
- Sistema de citas en linea exclusivo para Centro Medico de Caracas en San Bernardino
- Citas CMDLT: Jueves. llamar al 0212-9496243 y 9496245
- Las Emergencias son atendidas en CMDLT previa coordinacion personal al 04142708338
- Proveedor Seguros Mercantil y Sudeban

Due to the dramatic bodily changes that a woman undergoes during pregnancy, it is natural that joint and muscular discomfort occur. Their frequency is high but fortunately they are mild or moderate in intensity and rarely incapacitate the patient.
Sequence of nuisances during pregnancy
First Trimester: weeks 0 to 12
During this period there are no particular musculoskeletal complaints attributable to pregnancy because the major changes associated with fetal growth have not yet occurred. This period is full of symptoms that suggest the presence of pregnancy: nausea, vomiting, dizziness, drowsiness, feeling of weight and breast tenderness and internal pelvic discomfort.
Second Trimester: weeks 13 to 25
By the middle of the second trimester, the musculoskeletal complaints that will affect at least 50% of pregnant women begin to manifest themselves. These appear gradually and in different anatomical locations, most of them are mild, but can sometimes significantly compromise the quality of daily life of the pregnant woman.
The origin of these symptoms during this period is the accelerated uterine growth and the joint relaxing effect of some of the pregnancy hormones, especially relaxin and progesterone
Round ligament pain: typically appears between weeks 16-20 of pregnancy, very common (I would say that more than 70% of patients report it), is located in one or both groins (especially the right) and is frequently associated with daily physical activity. It appears frequently after a day of hard work, unusually intense physical activity or when there have been prolonged standing postures, it is reported as menstrual or pelvic pain or pain “in the ovaries”
It is due to the traction, elongation and spasms of the round ligaments of the uterus in its attempt to stabilize the uterus after a sudden uterine movement caused by rapid changes of position such as getting up hastily from a chair or bed
Pubic pain, pubalgia: this condition is very frequent and its appearance is later than the pain of the round ligament, it is due to the separation and partial instability of the pubic bone joint due to joint relaxation promoted by relaxin (a hormone of ovarian origin) in preparation for the vaginal delivery process. This pain occurs in the midline below the navel on the Mons Pubis as a result of excess activity, spending long time in the same position (sitting or standing), when getting out of bed in a forward motion (like doing abs) and for going up and down stairs. It can be extremely annoying and many patients can confuse it with a labor, but unlike the latter, the pubic pain is continuous; the pubic pain point is the most important data to differentiate one from the other, pressing the pubis elicits or exacerbates pain
Third Trimester: weeks 26 to 40
The last 13 weeks of pregnancy are characterized by marked abdominal growth, fluid retention, joint overload and changes in the dynamic and static function of the spine
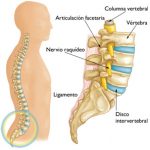
Lumbago: or lower back pain is due to the change of body posture secondary to abdominal growth and the compensatory mechanisms of the joints and muscles of the spine (change of the center of gravity). Pain occurs in the center of the back above the level of the buttocks, it is continuous, improves with rest and worsens with certain prolonged postures or excessive physical activity. Picking up things from the floor by bending the body forward is detrimental to the lower back.
Sacroiliitis: it is the swelling of the joints of the sacrum with the pelvis in the lower back, unlike the lumbago this pain is presented to the sides and not in the center, especially on the right side. It is stinging and can become very annoying. Some maneuvers practiced by the obstetrician elicit pain and establish the precise diagnosis
Pubalgia: as the pregnancy progresses the pubic pain can become more noticeable and annoying, it comes and goes episodically in relation to the physical activity or the bad postures of the day
Cramps in lower limbs: these occur as painful and involuntary contractions in one or both calves, occur preferably during the night when the patient is lying down, sleeping, usually past midnight. Its origin is unknown and there is no effective treatment. One of the measures that has offered some improvement has been instructing the patient to exercise (walking, swimming) during the day.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: this condition manifests itself with numbness, tingling or pain in the fingers of the hands, especially the 2 central ones. It is due to the accumulation of fluid at the level of the wrists and compression of the nerves that innervate the central fingers of the hand (median nerve). It is a benign but annoying condition that improves by raising the arms above the cardiac level and repeating cycles of opening and closing (clenching) of the hands, in this way the edema fluid is expelled eliminating its compressive effect. In severe cases, surgical decompression may be required.
General measures
- If you have any doubt, call your symptoms to your doctor.
- Exercise reasonably during the day to tone up your muscles (swimming is excellent, walking is great).
- Maintain ergonomic postures at work, avoid keeping your legs crossed.
- Wear shoes with low heels: flat sandals generate foot and tendon pain, and very high heels are unstable and increase the risk of accidents
- Do not bend forward to pick up items from the floor, bend your knees and lower/raise keeping your back straight.
- In case of unilateral pain, sleep on the opposite side of the pain.
- To leave your bed: roll to one side, lower your legs and sit up (thus avoiding traction on the pubis).
- Place pillows strategically on your back, between your legs, neck and arms.
- Avoid carrying excessive weight loads.
- To mitigate pelvic and lumbar pain, lie on one side in a fetal position with a pillow between your knees and another under your belly for better support. Resting 30-60 minutes does wonders!
- If pain is intense your doctor will indicate analgesia, some special measures or physiotherapy. Sometimes you have to go to an Orthopedist or Chiropractor.
Back pain and other discomforts are a small price to pay for the miracle of a new life.
- .
Lumbago, back pain and sciatica
The emotion of becoming a mother can be overshadowed by back pain and sciatica. Three out of four pregnant women experience back pain. I hope this information is useful to avoid or overcome this condition.
How does pregnancy cause back pain and sciatica?
Changes in your body throughout pregnancy affect more than just your looks
1. Weight gain, about 10 Kg. or more. The increase in body weight puts pressure on the lumbar discs in the lower back. Back and leg pain (sciatica) are common.
2. Weight gain can lead to piriformis syndrome and sciatica. The piriform muscles, located in the buttocks, help the movement of the thigh. Piriformis Syndrome can develop when the muscle compresses the sciatic nerve, which passes through the buttocks on its way to the thighs.
3. As the uterus grows the center of gravity of the body changes generating responses that can be painful. Sometimes, as the uterus expands inside the pelvis, it compresses the spinal nerves in the lumbar and sacral regions of the spine generating pain
4. Relaxin, a hormone that relaxes the joint ligaments in preparation for childbirth, allows a greater lassitude and joint instability that can generate pain. It is important that you know how to exercise or lift objects, because it is easy to get injured during pregnancy. Move slowly and avoid sudden movements.
What to do
- Keep your weight controlled.
- Call your doctor if there is back pain
- Take care of your posture! Stand up straight, with your shoulders back, your buttocks contracted and avoid leaning forward.
- Simple cardio exercises such as walking and/or swimming will help you stay in shape.
- Prenatal massage can help relieve pain and tension. Masseuses trained in Prenatal Massage can be a source of relief during pregnancy and labor.
- A warm shower is excellent.
Ergonomic suggestions: at work, at home, at leisure.
Prospective mothers should avoid uncomfortable postures, extreme efforts such as lifting heavy objects and repetitive tasks, especially during the third trimester. In the last part of pregnancy, the woman’s body faces its greatest challenges, ergonomically speaking.
- The muscles of the lower back and legs work harder to maintain balance. Simply standing or walking can be a challenge. Swelling of the extremities is common. It is very useful to rest and take frequent short breaks (raising the feet).
- An ergonomically designed and adjustable chair, with support for the lower back and feet, can make desk work more comfortable. Change your posture by sitting up and standing up frequently.
- If your task requires you to be seated, take periodic breaks to walk. Walking helps reduce swelling by increasing circulation and venous return. Hopefully, you will be one of the few future moms whose pregnancy progresses without back pain or sciatica. But remember that if back pain starts, you should notify your doctor