- Citas Centro Médico de Caracas: Lunes, Miercoles y Viernes. Pulse el botón Agende una Cita
- Sistema de citas en linea exclusivo para Centro Medico de Caracas en San Bernardino
- Citas CMDLT: Jueves. llamar al 0212-9496243 y 9496245
- Las Emergencias son atendidas en CMDLT previa coordinacion personal al 04142708338
- Proveedor Seguros Mercantil y Sudeban
It is the specialized ultrasound study of the baby’s heart made by professionals trained in the area. It is not a routine study and is only practiced if there is any indication for such an effect: family or personal history of congenital heart disease or suspicious ultrasound findings during routine evaluations.
However, the Fetal Medicine Foundation of the United Kingdom offers online certification courses to universalize the fetal cardiac study and make it an integral part of the routine evaluation of the fetus, the idea is to improve the detection rates of heart diseases during pregnancy and eliminate the taboo that limited the cardiac diagnostic capacity of the general obstetrician . We have already completed the evaluation of the normal heart in all the necessary parameters to determine the normality of the organ during the routine evaluation of the fetus from 17 to 23 weeks; if a complex anomaly is found, we refer the patient to a qualified specialist to obtain the definitive diagnosis / prognosis.
With high resolution ultrasound equipment it is now possible to visualize and examine the heart in the fetal growth phases in the general population. The anatomical knowledge of cardiac structures and the correct interpretation of echocardiographic images during fetal development allow the early diagnosis of certain congenital conditions with important physiopathological implications and opens the possibility of planning the most appropriate form and time for birth and providing early treatment of the newborn.
The decision of the management of the fetus at the moment in which a congenital heart anomaly is recognized must be taken by a multidisciplinary team that allows coordinated action after birth. Fetal echocardiography is becoming a valuable tool in the management of congenital malformations in general, which represent the main cause of mortality among newborns, and to evaluate and deepen the knowledge of the natural history of cardiac malformations. more frequent among the congenital. There is no doubt that the use and knowledge of this imaging technique by general obstetricians will improve the survival of newborns with certain congenital heart anomalies and will have a significant impact on the long-term clinical outcome and on the quality of life of patients.
Ultrasound diagnosis is based on the recognition of normal patterns.
Cardiac malformations occur in approximately 8/1000 live births, but a much higher frequency is estimated if abortions and in utero deaths are considered.
Technical data in the evaluation of the normal fetal heart
- A cross section of the upper part of the abdomen shows the stomach to the left of the fetus and the correct horizontal plane demonstrates the circular shape of the thorax and an almost complete rib. The image, a few millimeters above the stomach, allows to obtain the basic cut of the 4 cardiac chambers, point from which the evaluation is developed.
- The abdominal aorta is located to the left of the vertebral column and the inferior vena cava to the right of the aorta. In front of them the heart, with its 4 cameras, the most important cut of the evaluation and seating of 60% of the diagnoses of major cardiac malformations. The remaining 40% of the malformations can be seen in the appropriate cuts of the great vessels and the complementary cuts.
- The heart is located in the left thorax within its normal axis (around 45 degrees) and occupies approximately one third of the thorax.
- The atria, ventricles, and orifices of the right and left atrioventricular valves (tricuspid and mitral, respectively) are approximately the same size.
- The ventricular walls and the interventricular septum are approximately the same thickness.
- The moderating band, a morphological marker of the right ventricle, is a muscle bundle at the apex of the right ventricle.
- There is an intact interventricular septum and on which the atrioventricular valves are implanted (the tricuspid is a little lower -apical- than the mitral valve).
- The foramen ovale occupies approximately one third of the atrial septum and has a valve that identifies the left atrium (septum primum).
- The connection of the right and left pulmonary veins in the posterior part of the left atrium on both sides of the descending aorta is seen.
- The aorta emerges from the left ventricle and to the right, the pulmonary, superior to it emerges from the right ventricle to the left forming the so-called crossing of the great vessels.
- In a more superior cut we see the sign of the V, the aortic arch and the pulmonary/ductus arteriosus.
- The uppermost cut evidences aortic arch and trachea from behind.
- From the arch you can see the exit of 3 vessels that go to the neck and right arm.
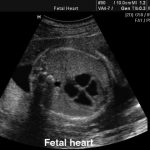
Fetal heart
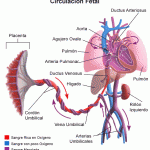
Fetal Circulation: A system designed to limit the flow of blood to the lungs since they will not be used in gas exchange until birth.
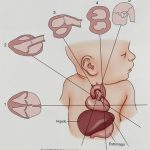
Fetal echocardio, main planes
- Four chamber
- Aorta, long axis.
- Pulmonary, long axis.
- Ventricles, short axis.
- Large vessels, short axis.
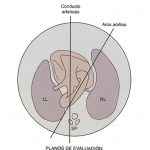
Fetal echocardio, complementary planes:
- Ductus arteriosus, ductal arch.
- Aortic arch.
Cross section of the thorax demonstrating the 4 heart chambers (2 ventricles and 2 atria) in normal orientation with 45 degrees of rotation.