- Citas Centro Médico de Caracas: Lunes, Miercoles y Viernes. Pulse el botón Agende una Cita
- Sistema de citas en linea exclusivo para Centro Medico de Caracas en San Bernardino
- Citas CMDLT: Jueves. llamar al 0212-9496243 y 9496245
- Las Emergencias son atendidas en CMDLT previa coordinacion personal al 04142708338
- Proveedor Seguros Mercantil y Sudeban

Vaginal birth is the natural reproduction mechanism of the human species, how natural it depends on the expectations and beliefs of the family nucleus involved, for biology all vaginal birth is natural, now, depending on the particular expectations we have natural births without assistance of any species until the natural births monitored and attended by a specialist in obstetrics following all the norms of control of modern and updated medicine
The truth is that, however it may be and despite criticism of modern obstetrics and modern modes of birth, maternal-fetal morbidity and mortality have declined dramatically in the last 300 years (maternal mortality: 1400 to 11 per 100,000 live births) and the most important reasons are: hygiene of the doctor (hand washing, Semmelweis, 1818-1865 ), invention and use of gloves (Bloodgood, 1893), prenatal control (Ballantyne, 1901), antibiotics (Penicillin 1928) , anesthetic techniques, safe cesarean section (1940), fetal monitoring and ultrasonography
This whole introduction aims to make it clear that natural childbirth is not a unique concept, unlike what vaginal birth means, which only and clearly suggests that the baby was born or will be born through the vagina. From now on I will talk about the essence of vaginal delivery and its mechanism, leaving aside the discussions about its naturalness. Later I will develop some of these controversies and points of view.
Definitions
Cephalic presentation : baby head. The fetus is in proper position for vaginal delivery by presenting its head to the birth canal
Breech presentation: baby seated. The fetus presents the buttocks or variants (feet, knees) in the direction of the birth canal. It is not a good preparation to give birth so many obstetricians will decide to perform a cesarean to avoid injuries and fetal or maternal complications that are known to increase in this type of delivery
Premature or preterm labor: delivery that is consumed before 37 weeks of gestation.
Delivery : Delivery occurs at any time from week 37 but before week 42 of gestation.
Post-term or post-mature delivery : is that which occurs on or after the 42nd week of gestation.
Braxton-Hicks contractions: are the uterine contractions that are present towards the end of pregnancy and that despite being notorious and recognized by the mother do not generate pain and are inefficient to lead to delivery, although they precede it. Characteristics: the uterus becomes hard and rounded and can feel like a big rigid ball inside the maternal abdomen without generating pain, duration less than 30 seconds and without a defined pattern in time. The common antispasmodics eliminate them, false labor
Uterine Contractions: is any contraction of the uterus, but when we refer to them in a generic way we are usually talking about the contractions associated with labor. These contractions are manifested as those of Braxton-Hicks but are more durable (more than 30 seconds), are accompanied by menstrual abdominal pain with discomfort in the lower abdomen and then in the lower abdomen and lower back (lumbar), intensity and increasing frequency. Once they start they are not eliminated with common antispasmodics, true labor
Labor: it is the process by means of which the baby is expelled of the maternal matrix thanks to the expulsive contractions of the uterus that are causing the descent of the baby and the dilation of the uterine neck. The labor of childbirth is longer in gilts and shorter in multiparous
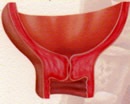
Vaginal canal: canal through which the baby will be born, formed by the vagina and the dilated remnant of the cervix and the bony structures that give origin to the female pelvis. Journey that the baby has to follow to get out through the vulva
Dilation : the opening of the cervix during labor. It is the manifestation of the pressure exerted by the baby on the cervix due to the force of the uterine contractions. The real labor is one that invariably leads to a birth, the false labor is one that could be stopped and only remained as a threat of birth.
Effacement: uterine contractions make the cervix progressively shorter and effaced.. The first first clears the entire neck and then dilates. The multipara effaces and dilates at the same time.
Bloody show: is the vaginal expulsion of a little amount of blood-satined mucus through the vagina. It is the first sign of the beginning of the changes of the cervix before delivery. When the effacement and dilation of the cervix begin, the mucus that occludes the canal is expelled in the form of a thick mucous vaginal discharge and tingled with blood, like jelly.
Vaginal exam: it is the digital exploration of the birth canal and the evaluation of the conditions of the cervix and descent of the baby to follow the progression of labor.
Engagement: this is a distinctly obstetric term that refers to the descent of the fetal head within the maternal pelvis. By the time the breakdown occurs and the head is deeply descended in the maternal pelvis and the neck is fully dilated (10 cm). What many women call embedding are the pains that the fetal head causes due to the pressure exerted on the bladder or pubic bones but this is not correct.
Expulsive: is the phase of labor that runs between full dilation (the famous 10 centimeters) and the expulsion or birth of the baby. This phase lasts less than 1 hour in most births, usually 15-30 minutes. Beyond 1 hour we began to consider a “prolonged expulsive”. This is giving birth
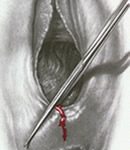
Episiotomy: is the cut that is practiced in the posterior angle of the vagina (above the anus) in order to allow a faster expulsion of the baby and avoid uncontrolled tears of the genital and rectal regions.
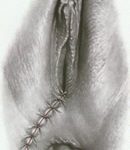
Episiorrhaphy: is the repair, by using sutures, of the wound left by the episiotomy. We use absorbable suture that melts by itself and does not need to be removed later
Placental expulsion: is the expulsion of the placenta from the mother’s womb. Of good law means “to give birth” so that it is a mistake to say for example, Maria gave birth to a man, because in reality she gave birth to a placenta. It happens that many people find it impolite to say “give birth” to a baby and choose to say “give birth”.
Instrumental childbirth: it is where the process of childbirth (expulsion of the baby) is completed through the application of the Obstetric Forceps or some of its variants including cephalic suction devices. Currently, its indications have been greatly reduced since cesarean section became a safer procedure than the application of a difficult forceps. In good hands and following the precise indications this instrument is excellent and very far from the bad reputation that precedes it
Fetal-pelvic disproportion (FPD) : is the term we use to express that the dimensions of the fetal head are greater than those of the pelvic structures of the birth canal. This narrowness would prevent the vaginal birth of the baby and is an indication of cesarean section.
Bishop’s score: this is a score system that considers 5 elements of the vaginal exam to predict the possibility of success in the Labor Labor Induction and the prediction of an imminent and successful spontaneous labor.
A score of 6 or less suggests that the spontaneous onset of labor is unlikely and likely to be unsuccessful either because labor is not successful or because labor is unsuccessful and does not lead to vaginal delivery . This, the success, varies a lot depending on the resources available in the Care Center and the tolerance level for prolonged events (births of days)
A score of 9 or more indicates that the onset of labor will probably begin spontaneously and that you will have a high chance of leading to a vaginal birth
Some authors suggest that only a score of 8 or higher is reliable to predict successful induction.
Am I giving birth?
This is always a very good question, whose answer, unfortunately we Obstetricians take for granted. We talk so much about contractions and labor that we forget that the patient, the first-timer, has no idea what it is about. Every woman who starts a labor sooner or later will know (of course, it ends with the birth of a baby, something that can not be hidden), the idea is to know it early so you can take the necessary measures
We are going to do an exercise: Touch your abdomen and try to feel your baby, most of the day you can feel small, rounded parts that move or move because your uterus is soft and relaxed. Several times during the day you will notice that your “belly” gets hard, it goes down a little, it is rounded like a well-defined soccer ball and when trying to touch parts of the baby you can not do it because it has formed a kind of dome that it prevents you from having access to it. This is a uterine contraction
The contractions that occur throughout pregnancy begin to become noticeable at the end of pregnancy, the mother only realizes them to see or touch the “belly” (with the features described above), but do not hurt, come and go variable way and last less than 30 seconds. These are the preparatory contractions, Braxton-Hicks
The pain
The labor pains will sooner or later occur in most pregnant women and manifest themselves in a somewhat different pattern to that described for the Braxton-Hicks, although in essence they are the same: uterine contractions. What is the difference? The intensity, the power of the contractions, their regularity and their effect on the cervix. When the time comes, and by mechanisms that we do not yet know, the isolated uterine contractions synchronize, become more intense, last more than 30 seconds (45 to 60 seconds), become more painful as time goes on and instead of Occurring sporadically they begin to follow a regular pattern that is becoming more frequent. At this point we refer to the contractions as each episode of abdominal pain that the patient presents.
The pain initially presents below the navel, as a menstrual type colic and later it will become more frequent and intense and after a few hours will be added lower back pain, lumbopelvic pain of labor by cervical dilation
What is the bloody show, the mucous plug?
The famous plug is the expulsion of mucus, stained with a small amount of blood, by the genitals of the pregnant woman before or after the uterine contractions have begun. This spot or Blood Sign (Bloody Show, of the Anglo-Saxons) suggests the beginning of changes or modifications of the cervix that begin before delivery
Typical case
You are calm in your house sleeping despite the “potbellied”, at about 1 in the morning you wake up for abdominal discomfort, wanting to pee and feeling wet on your genitals. You gets out of bed, go to the bathroom and starts to evacuate your bladder, feel better, clean up and … horror! blood and mucus like jam in the toilet paper. Wake up your husband, who between asleep and awake tells you that it is nothing and goes to bed again. Well, since you don’t feel bad, you go back to bed; in addition, your husband must know what he says…
An hour later you wake up again with abdominal pain, menstrual like pain, you go to the bathroom again: a little more of that red jelly when you clean up. The pain subsides. You dont wake your husband this time, he is tired “the poor one”. You go back to bed.
In forty-five minutes you are in pain again. Again, pain at 30 minutes, again in the bathroom: What ‘s happening here? I’m giving birth ! you answer.
You wake up your husband, you say: I’m giving birth! The guy now wakes up startled. While both are thinking about the next step, the pain returns in 25 minutes, stronger and with back pain.
Your husband calls the doctor. They agree to see each other in the clinic, contractions are more frequent and painful as time goes by. At 5 o’clock in the morning they have everything ready, the pains have come and gone every 20 minutes, each time stronger and more durable, you have wanted to pee on several occasions, you go to the clinic … a spectacular baby is born at 2:41 in the afternoon!
Other manifestations and atypical cases
Loss of fluid by genitals: rupture of membranes (breaking sources) can occur before the onset of contractions. This is presented as the sudden exit of abundant fluid through the vagina, the bed or clothes get wet or the liquid slides down the legs. It has a smell similar to semen or chlorine. If this happens, notify your doctor immediately, especially if your pregnancy is less than 37 weeks old. Contractions start minutes to hours after the break.
Pain-free contractions: Some women, especially multiparous women, may present effective uterine contractions for labor without severe pain. This is rarely seen in gilts. There is no way to know which patients will behave in this way. In these cases, alternative signs such as expulsion of the stopper or loss of fluid are pending. As I said, fortunately this is quite rare, if you have any questions, ask your obstetrician.
WARNING: This is the case of a full-term pregnancy, with more than 37 weeks, with a mature baby ready to be born. If this occurs before 37 weeks of gestation we would be in the presence of a Preterm Birth and you should notify your obstetrician immediately and go to the clinic or hospital without delay; the mere fact of expelling some mucus with blood through the genitals before 37 weeks of pregnancy is sufficient reason to notify your doctor.
Some steps
Epidural anesthesia: so that labor and fetal expulsion are tolerable.
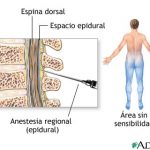
Perianalgesia
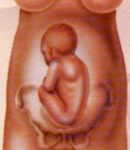
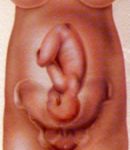 Cephalic Presentation: childbirth
Cephalic Presentation: childbirth
 Breech presentation: cesarean section
Breech presentation: cesarean section
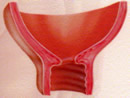
Start of dilation, cervix short and effaced 90%
Complete dilatation, expulsive, 10 cm
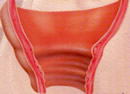
Descent of the fetal head in the birth canal
Episiotomy: avoid perineal tears
Episiorrhaphy: perineal repair
Conservative active management
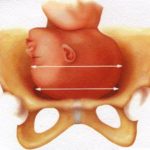
Baby in ideal position for vaginal delivery: Left Cephalic.
After the end of pregnancy, beyond week 37 (especially after 38), the first genital touch is performed with the intention of evaluating the relationship of the fetal head with the pelvic diameters and the characteristics of the cervix. . With the information obtained, preliminary data on the possibilities of a vaginal delivery or cesarean section can be obtained.
If conditions permit, this is the time to perform the amniotic membrane decoration , a procedure that will help to initiate a progressive labor due to the maturation of the cervix and the generation of asymptomatic uterine contractions in the patient that will eventually lead to a firmly established labor. The advantage of this procedure is that it induces work naturally.
This procedure is only practiced in those women who do not have contraindications for vaginal delivery.
Decolage is not harmful for the mother or fetus, does not disrupt the membranes so that the baby is still immersed in a sterile environment.
Typically the patient enters with 4-7 cm of dilation, conductive analgesia is placed and labor is conducted with low doses of oxytocin to obtain rhythmic and regular contractions.