- Citas Centro Médico de Caracas: Lunes, Miercoles y Viernes. Pulse el botón Agende una Cita
- Sistema de citas en linea exclusivo para Centro Medico de Caracas en San Bernardino
- Citas CMDLT: Jueves. llamar al 0212-9496243 y 9496245
- Las Emergencias son atendidas en CMDLT previa coordinacion personal al 04142708338
- Proveedor Seguros Mercantil y Sudeban

Should you have a special diet during pregnancy?
This is the question of many women once they find out their status. Actually the diet must be simply balanced and we must eliminate the myth that we now have to eat twice as much. Actually, it is after the third month of pregnancy that the requirements increase by 300 calories over the requirement of any woman, that is, if my normal requirement is 1500 calories; After the third month of pregnancy, I must ingest 1800 calories, which will satisfy the needs of the growing fetus and the changes in the mother’s body. Good nutrition will help prevent in the mother, anemia, infections and poor tissue healing after childbirth.
Lic. M. Gabriela Galarza.
Clinical Nutritionist
A balanced diet
The concept of Balanced Diet has its origin in the correct selection of the appropriate portions of each type of food depending on the daily requirements of each person according to their individual characteristics
The nutrient intake should follow the same guidelines as the nutritional pyramid based on the group of bread, pasta, and cereals, suggesting a daily intake of 7 servings per day. In the next position are the vegetables and fruits of which you should eat an average of 4 servings a day between the two. Then there is the group of eggs, grains, meats and it is suggested to consume at least 3 servings a day. You should also eat 2 servings of dairy a day, including milk and milk products.
At the top of the pyramid we find saturated fats and fast-absorbing carbohydrates such as refined sugar, pastry sweets, fried foods, which should have a controlled intake.
Do I need vitamin supplementation? What vitamins to take during pregnancy?
The consumption of vitamin supplements is suggested from the moment you want to get pregnant. Supplements containing folic acid and other essential vitamins and minerals that will be mentioned later. Actually the requirements of certain vitamins and minerals are so increased during pregnancy that it is very difficult to meet the requirements only with food, however everything in excess is harmful, so you should not produce hypervitaminosis, it is ideal to always consult your doctor.
These needs in nutrients (proteins, fats and carbohydrates) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), advance according to the time of gestation. It is in the last three months where there is a noticeable fetal growth and when the fetal requirement is higher in energy, vitamins (A, E and C, folic acid, thiamine, riboflavin, pyridoxine, niacin and B12) and minerals (calcium, phosphorus, iron, zinc, iodine, magnesium, selenium). While during the first quarter the demands are not very considerable. If the mother does not cover her needs, the fetus may not suffer, but the mother may have a risk of anemia or risk of hemorrhaging.
What should my weight gain be in pregnancy?
Before making any recommendation on weight gain during pregnancy , you should take into account the weight of the mother before pregnancy, to know if there is a deficit or an excess. According to the body mass index, we can know it. This index combines the weight and height of the woman, so that the weight gain at the end will depend on the body mass index (BMI).
BMI of Low Weight (<19.8): it is suggested to gain from 12.5 to 18 Kg.
BMI of Normal Weight (19.8 – 26.0): suggested gain of 11 to 16 Kg.
BMI of Overweight (30 – 34.9): suggested gain of 6 to 11 Kg.
BMI of Obesity (> 30): suggested gain of 5 to 9 Kg *
These recommendations are different when we talk about teenagers.
Weight definitely has an influence on the evolution of pregnancy, it can influence the mother’s renal function, the lung capacity and the mother’s heart rate.
However, just as excess weight is bad, so is low weight
* Current literature suggests that overweight patients can establish a nutritional regimen that allows them to lose weight during pregnancy without adverse effects to the fetus; in fact, research suggests important maternal-fetal benefits.
What to do with nausea, vomiting and other discomfort?
These are the most common discomforts during the first trimester. In controlled cases, they do not produce significant alterations in the nutritional status of the mother or fetus unless they become uncontrollable.
There may also be other symptoms such as constipation, most of the time caused by iron supplements, in these cases the consumption of high fiber products such as wheat bran, whole products, raw or lightly cooked vegetables is suggested. steam, consume fruits with the skin and the consumption of water or drinks such as juices, infusions, etc. Exercise helps tone the bowel. Another common problem is acid reflux, in these cases do not wear tight clothing, dine two hours before going to sleep, eat frequent and in small portions, eat low fat do not consume plenty of liquid with meals, thus avoiding gastric distension. If this does not help, you should consult with your treating doctor, who will indicate pharmacological treatment if necessary.
What’s up with the cravings?
This urge to consume some kind of special meals, in most cases, may have its physiological reason, due to the deficiency of specific nutrients, such as magnesium, so some women who were not in the habit of consuming chocolate , now during pregnancy, they do it daily. However, there are no studies to prove it.
Coffee, Tea, Chocolate and other drinks with caffeine: In reasonable and relatively low doses there is no contraindication to the use of these beverages. The recommendation of the American School is to consume less than 200 mg of caffeine per day in any of its forms. Te: 50 mg (2 cups). Coffee: 50-100 mg (1-2 cups). Chocolate: 30 mg Refreshments: 37 mg
Canned: there is no contraindication as long as its consumption is within reasonable limits. It is always better to eat fresh foods.
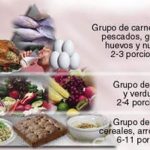
Nutritional pyramid
Nutritional pyramid in pregnancy, indicated portions of each row.
Line 1 : Foods of animal origin, fried foods, grains and nuts, high content of proteins and fats.
Dairy & Meat
2-3 servings a day


Line 2 : Foods with high content of complex sugars, fiber and water
2-4 servings daily

Line 3 : Foods based on cereals and flours. High content of complex carbohydrates and natural fiber

recommendations
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are expected elements of normal pregnancy, in fact it is suggested that they are an evolutionary adaptation to prevent the mother from being exposed to the intake of substances dangerous to the baby and that typically have strong odors or flavors.
So, do not see them as something bad but as a protective event; but because they can get to bother enough we give you some recommendations:
- Eat starchy foods, such as toast or crackers when you get up or when you feel nauseous.
- Do not drink large amounts of fluids in the morning or when you feel nauseated (you can take them at another time).
- Eat small and frequent rations (every 3 hours).
- Do not omit any food because when the sensation of hunger is intense, nausea is also intense. You can have cereal with milk, a small sandwich or a glass of yogurt before bedtime.
- Avoid sudden movements.
- Decrease foods high in fat or fried.
- Keep the environment ventilated and without strong odors.
- Try to eat cold dishes and foods with little aroma.
- Do not brush your teeth immediately after eating.
- There are certain women who find relief with the use of ginger as an infusion.
Recommendations for nausea and vomiting
Vitamin D
Recent research suggests that daily supplementation of high doses of vitamin D during pregnancy has many beneficial effects for the mother and fetus. Traditionally, 400-800 IU / day have been indicated, but currently the use of 4000-6000 IU / day is being suggested. The benefits are up to 50% fewer cases of Preeclampsia, Gestational Diabetes, Preterm Birth and infections and better neonatal evolution. If you want to participate you will be given 1000-4000 IU / day after evaluating your levels of Vitamin D in blood.
A recent study showed a 28% decrease in risk in fetal growth disorders and a 65% reduction in the risk of fetal and neonatal mortality with the use of 2000 mUI per day (the approximate dose indicated)
Association Between Vitamin D Supplementation During Pregnancy and Offspring Growth, Morbidity, and Mortality. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Wei Guang Bi, BSc. et al. May 29, 2018
Last revision: May 2018