- Citas Centro Médico de Caracas: Lunes, Miercoles y Viernes. Pulse el botón Agende una Cita
- Sistema de citas en linea exclusivo para Centro Medico de Caracas en San Bernardino
- Citas CMDLT: Jueves. llamar al 0212-9496243 y 9496245
- Las Emergencias son atendidas en CMDLT previa coordinacion personal al 04142708338
- Proveedor Seguros Mercantil y Sudeban

Pregnancy is that, a pregnancy, not a disease! But it is filled with changes and annoyances, a little price to pay for a baby
Classically pregnancy has been divided into three major periods called Trimesters of Pregnancy that correspond, approximately, to thirteen weeks each: First Trimester (1T) from Last Menstrual Period (LMP) to week 13, Second Trimester (2T) from week 14 to 25 and Third Trimester (3T) from week 26 to week 40. This artificial division has its origin in certain elements of the development and maturation of the embryo and fetus and is of great use to prevent, guide, diagnose and predict certain alterations and diseases of each period. Likewise, it guides the preventive strategies and necessary evaluations that within each quarter we must plan to offer an adequate antenatal care.
Low blood pressure is a common condition throughout pregnancy, it is not uncommon to have blood pressure readings as low as 90/60 even 80/50 and be perfectly fine. It is never normal: > 140/90 mmHg.
First Trimester: weeks 0 to 13
It is characterized by the well-known symptomatology of dizziness, nausea and vomiting of pregnancy (NVP) and morning sickness that suggests the presence of a pregnancy. There may be menstrual type pelvic pain and unspecified low abdomen discomfort. Other: gas, indigestion, a lot or little appetite , abdominal distension, drowsiness, apathy, lack of concentration, melancholy. This elicits the question from a co-worker or friend, are you sure you are not pregnant?
Approximately 50% of pregnant women will experience nausea/vomiting of pregnancy (NVP) between weeks 6 and 16 and 1% will be so severe as to need hospitalization and nutritional assistance (Hyperemesis Gravidarum). These 13 weeks are the most important, since during this period all the fetal organs and systems are formed (organogenesis): all the congenital anomalies, chromosomal and genetic syndromes occur during this period, if we survive this trimester unharmed we will most likely have normal babies. At the end of this trimester the uterus feels like a small ball above the pubic bone. Although the patient may state otherwise, the baby can not be felt yet because its size and strength is insufficient to stimulate the uterus. Any bleeding during the first trimester is called Threatened Abortion, and is never considered normal. No baby born in this trimester will survive. The accelerated production of pregnancy hormones can generate psychological manifestations in women, melancholy, anguish and expectations about the future baby and sufficiency in the role of mother. Constant sleepiness, fatigue, lack of energy and occasional dyspnea are other frequently reported symptoms. Migraine may increase towards the end of this trimester and then decrease in the rest of the pregnancy. Postprandial Fullness refers to the feeling of fullness, dyspepsia, indigestion that is felt when eating normal amounts of food during the first weeks of pregnancy, this happens because the stomach takes more time to empty, staying full longer, this yields around week 16. During this trimester the 11-13.6 scan is performed, a sonographic evaluation of the fetus designed to rule out most fetal chromosomal and genetic syndromes and congenital malformations. Fetal sex is given in 95% of the patients with a 98% success rate. Cell free fetal DNA tests are performed during this trimester but they cost a lot
Second Trimester: weeks 14 to 25
During the first weeks of this period and until week 16 nausea/vomiting persist and gradually fade away. Inguinal discomfort can be manifested by pain in the round ligaments of the uterus and pubis. At the end of week 16 the uncomfortable symptoms of pregnancy will have yielded considerably and the mother will spend several weeks feeling great, with a small abdominal bulge that grows little by little until it becomes very noticeable. At some point between weeks 16-20 the future mom will feel the movements of her baby for the first time (Quickening).
During the next weeks we will observe the progressive growth of the belly and the baby and we will have a very good fetal ultrasound image that will allow us to complete the anatomical survey of the baby, something that could not be done while the baby was very small because some structures were not developed enough to be seen. By this time the sex of the baby has been diagnosed in 100% of cases in appropriate hands and most of the anatomical problems of the baby would have been ruled out. During this trimester, maternal serum screening tests for chromosomal anomalies and Spina Bifida are performed using maternal blood, amniocentesis (if there is an indication), screening for Gestational Diabetes and detection of risk of premature delivery are also carried out.
Third Trimester: weeks 26 to 40
By the time the third and last trimester begins, we begin to appreciate the progressive and remarkable increase in the weight of the baby thanks to the growth of internal organs, skeletal development and bone calcification, increase in muscle mass and the accumulation of subcutaneous fat, among others. At the beginning of the period the fetus weighs only 900 gr and will weigh, on average, 3500 gr before delivery. Most of the baby’s organs function as they will in adult life except for the Nervous System that will finally mature during the first years of life and the lungs that will only be in adequate maturity a few weeks before the birth of the baby. Ultimately the last necessary organs to mature for the immediate survival of the baby, the lungs, will do so at the end of pregnancy (from week 37) and their function will condition the survival of the newborn.
General symptoms: easy fatigue, daytime sleepiness, nocturnal insomnia, respiratory difficulties, fine motor clumsiness, joint instability, decreased ability to concentrate.
Abdominal Volume: the abdomen increases its volume quickly in this trimester thanks to the growth of the baby, the placenta and the amniotic fluid accumulation. The amniotic fluid will stop increasing at about week 34, and in fact will decrease considerably afterwards, but the baby will continue to gain weight at a rate of 150-200 gr per week. At the beginning of 3T the uterus reaches a little above the navel and at the end, near the end of pregnancy, it will reach the rib margin practically below the thorax. Near labor, the abdomen lowers its size because of the “Baby Droping”, the baby has begun to penetrate the pelvis.
Cardiovascular system: the main symptoms of this stage are related to Tachycardia and Hypotension. Since the uterus has grown and has considerable weight, the mother will not be able to lie on her back because it becomes uncomfortable and can cause a fall in blood pressure (Recumbent hypotension) due to the compression of the great abdominal vessels: sudden or rapid onset symptoms include shortness of breath, dizziness, blurred vision, feeling of imminent faintness, tachycardia, cold clammy skin, sweating, and nausea. Recovery is fast by rolling to one side or the other (right or left is the same). Drop of blood pressure related to leg blood stasis, Orthostatic Hypotension, occurs when the mother is standing for a long time, under the sun, in crowded places or when the mother stands up from the bed or chair abruptly. To recover you must sit down, in more severe cases you should lie down and raise your legs
Breasts: they have grown considerably, superficial venous circulation is visible, they are indurated and discretely sensitive (although not as much as as they were at the beginning of pregnancy), some women will have clear discharge from the nipples (Colostrum). Many women are concerned about the appearance of certain “little nodes” in the areolas; that change is normal and is due to the growth of the sebaceous glands of Montgomery that will lubricate the areola/nipple complex during lactation. The nipples and areolas grow in size and get pigmented of a brownish tone. All these changes vary from person to person and are partially reversible. They are ready, just waiting for the signal, the birth of your baby, to start producing milk.
Skin and Hair: due to the increase in uterine volume and the distension of the skin secondary to subcutaneous fat deposits the elastic support of the skin (elastin and collagen) tears giving rise to red striae below the navel, breasts, thighs and buttocks in susceptible women. In the skin of the cheeks may stain with a brown patch, the Chloasma Gravidarum, that can be partially avoided using sunscreen lotions (30-45) on a daily basis. The central line of the abdomen (Linea Alba) is pigmented giving rise to the Linea Nigra. Changes in hair and body hair can be remarkable: pregnancy stimulate hair production and growth, in some women can be seen varying degrees of hirsutism (excessive increase in body hair). The abrupt loss of hair observed in some women in the first four months postpartum is striking, although it is very frightening, it is self-limiting and full recovery is expected in 6 to 12 months. The sensation of heat and progressive reddening of the skin that is observed in pregnancy (especially in white skinned women) is due to vasodilation, one of the many effects of progesterone. For more information on pregnancy skin changes visit this article
Respiratory System: the respiratory manifestations of pregnancy began to be noticed from the beginning of pregnancy even when the “belly” was nonexistent. This is because the hormones of pregnancy, especially progesterone, have an effect on the respiratory system that stimulates breathing and somehow makes it conscious so that we notice that we breathe. Sighs, air hunger and fatigue are common too. During the last weeks of pregnancy dyspnea becomes more noticeable and increasingly intense because the lung capacity decreases considerably thanks to the pushing effect exerted by the uterus on the diaphragm. At this time, the future mom can’t do much exercise, gets tired with small exertion, especially when using stairs, and has a hard time sleeping without pillows, in fact, many patients use 2 or 3 pillows. The occurrence of snoring during sleep is frequent due to congestion, relaxation and narrowing of the maternal larynx.
Due to the generalized vasodilation of pregnancy, the arterial vessels of the nose that are responsible for heating and humidifying the inspired air bleed very easily so do not be frightened if on a dry, hot/cold day you bleed a bit through the nose (Epistaxis), this also explains why the nose grows during pregnancy. If bleeding is very heavy, call your obstetrician. This also explains the typical nasal obstruction of pregnancy. Many women complain about not being able to breathe, even thinking that they are drowning or suffering from an asthma attack. To prove that nothing serious is happening, breathe through your mouth as a test and you will acknowledge that there is no real respiratory obstruction. At night you can place a couple of drops of nasal decongestant (naphazoline) in each nostril to sleep better.
Towards the end of pregnancy, there may be pain in the area of the floating ribs because the uterus displaces the ribs forward and to the sides, generating local discomfort that increase when the patient lies down and improve while standing. Sometimes it manifests with acute back pain in the vertebro-costal joint due to dislocation of the lower ribs. This can be solved by pressing the affected rib inwards (or seeking the attention of an Orthopedist), it is quite rare and occurs more often in thin women with large babies.
Digestive system and oral cavity: due to the effect of hormones and the progressive effect of visceral displacement generated by the growing uterus, digestion slows down, satiety is obtained with increasingly smaller amounts of food, great heaviness after meals and heartburn and “burping” after eating certain strong flavored and spiced foods are very frequent. Constipation and gas (Meteorism) are common at the end of pregnancy, but they are easily managed with routine measures. Heartburn is actually due to the reflux of acid into the esophagus, a condition called Gastroesophageal Reflux (GERD). Antacid suspensions are excellent for treating this frequent problem, avoid lying down immediately after eating.
The gums during pregnancy are hypertrophic, enlarged, swollen, very vascularized and very delicate. It is not uncommon for the gums tend to bleed during tooth brushing. Although this does not represent disease, it is convenient to visit your dentist to rule out periodontal disease.
Urinary tract: the kidneys and urinary tract will be progressively compressed by the growing uterus, this results in altered drainage of urine, some dilation of the ureters, renal pelvis and poor bladder capacity to accommodate urine. This translates into urinary urgency and greater risk of urinary tract infections.
Weight gain and accumulation of fluid (edema): in general, a woman is expected to increase around 12 Kg during pregnancy. About half of that increase is due to the uterus and its contents and the rest is due to body fat and total water body content gain. It is natural to retain fluid since the metabolism of pregnancy requires a considerable increase in the liquid content of blood and other tissues. Visit this article for more info on weight gain during pregnancy
Round ligament
Pain of the Uterine Round Ligament typically appears between weeks 16-20, affects 70% of the patients, it is located in one or both groins (especially the right) and is associated with unusually intense physical activity, after a day of intense work or when standing for a long time, it is reported as menstrual pain, pain “in the ovaries” or colic.
It is due to the traction and spasms of the round ligaments of the uterus in its attempt to stabilize the uterus after a sudden uterine movement caused by rapid changes of position (getting out of a chair or bed), sneezing, laughing or coughing.
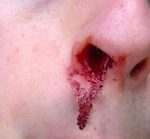
Epistaxis
Nasal bleeding, spontaneous or caused by sneezing or nose blowing, is frequent and expected during pregnancy due to arterial vasodilation. It is self-limiting and rarely requires medical attention.
Measures to stop bleeding: lower your head, press your nose and place local cold in your forehead and nasal bridge.
Notable changes
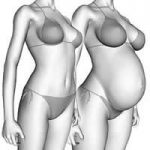
Increasing abdominal volume and weight moves the center of gravity of the body forward progressively generating compensatory adaptations in your posture:
- Greater lumbar curvature (lordosis) and back pain in 50% of pregnant women.
- Anterior correction of the neck (kyphosis) with greater risk of discomfort in the shoulders and arms (especially in computer users).
- Greater risk of accidents and falls due to instability, weight gain and joint laxity.
Very interesting video about abdominal growth in photos.